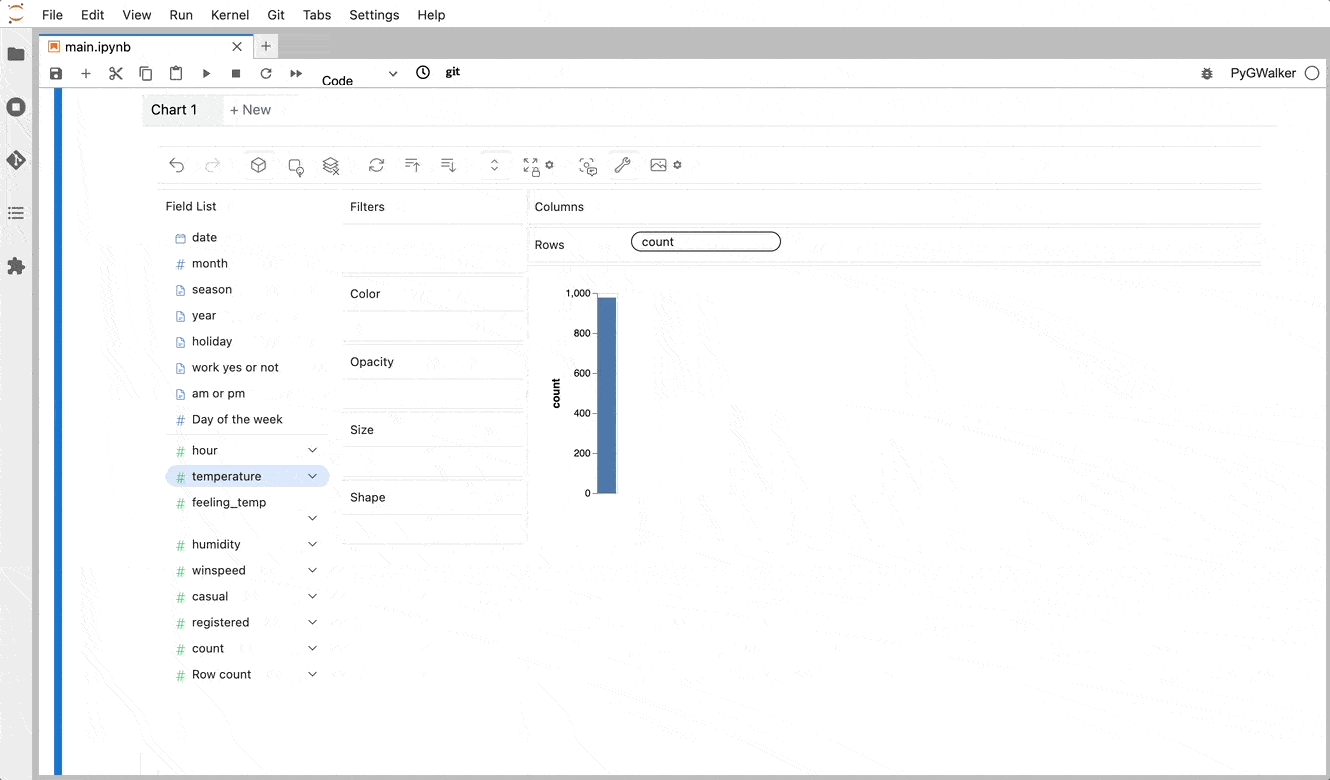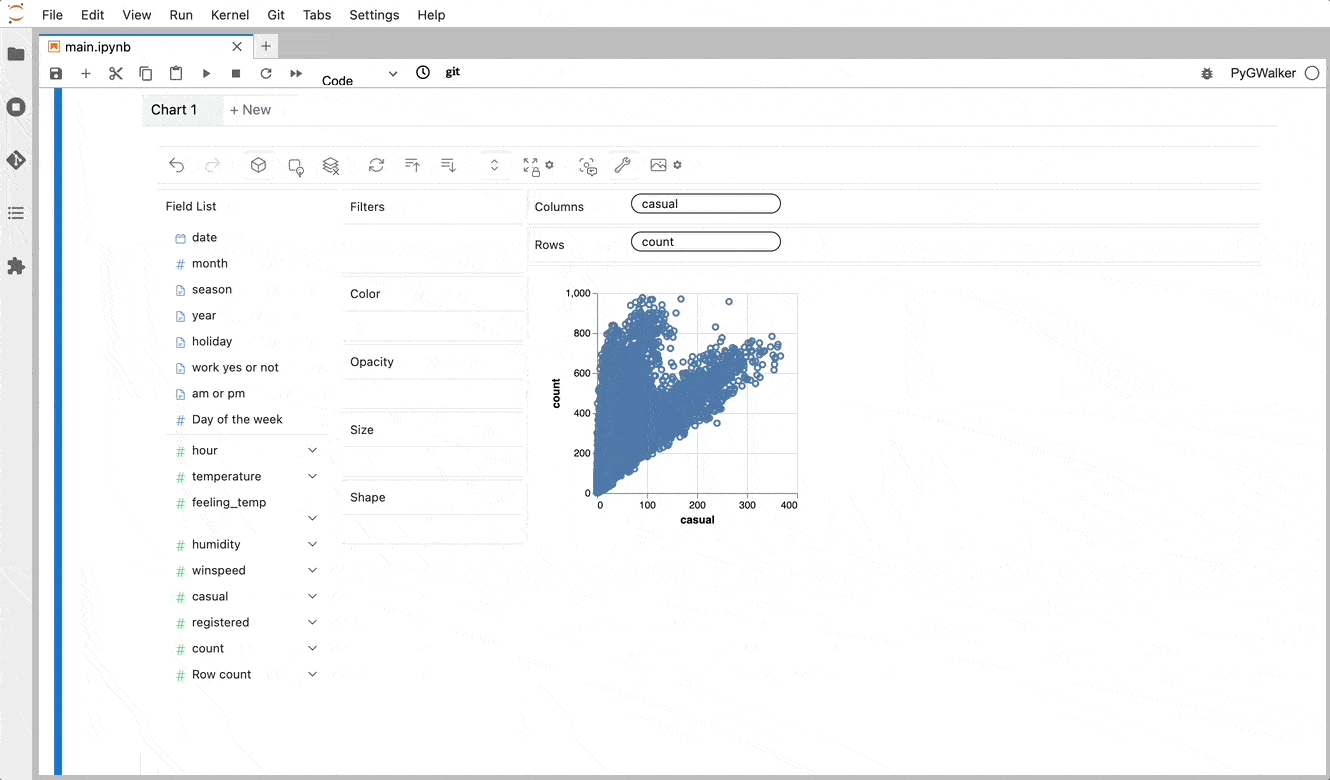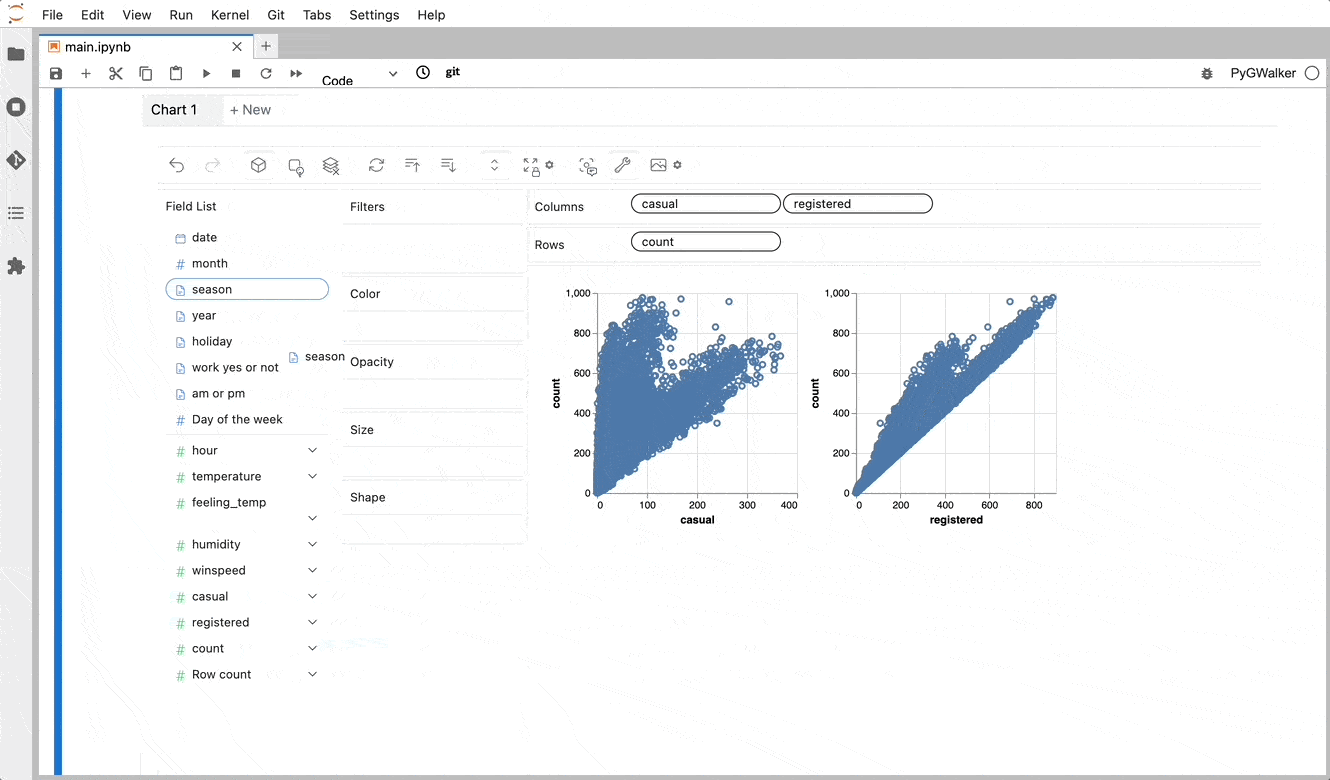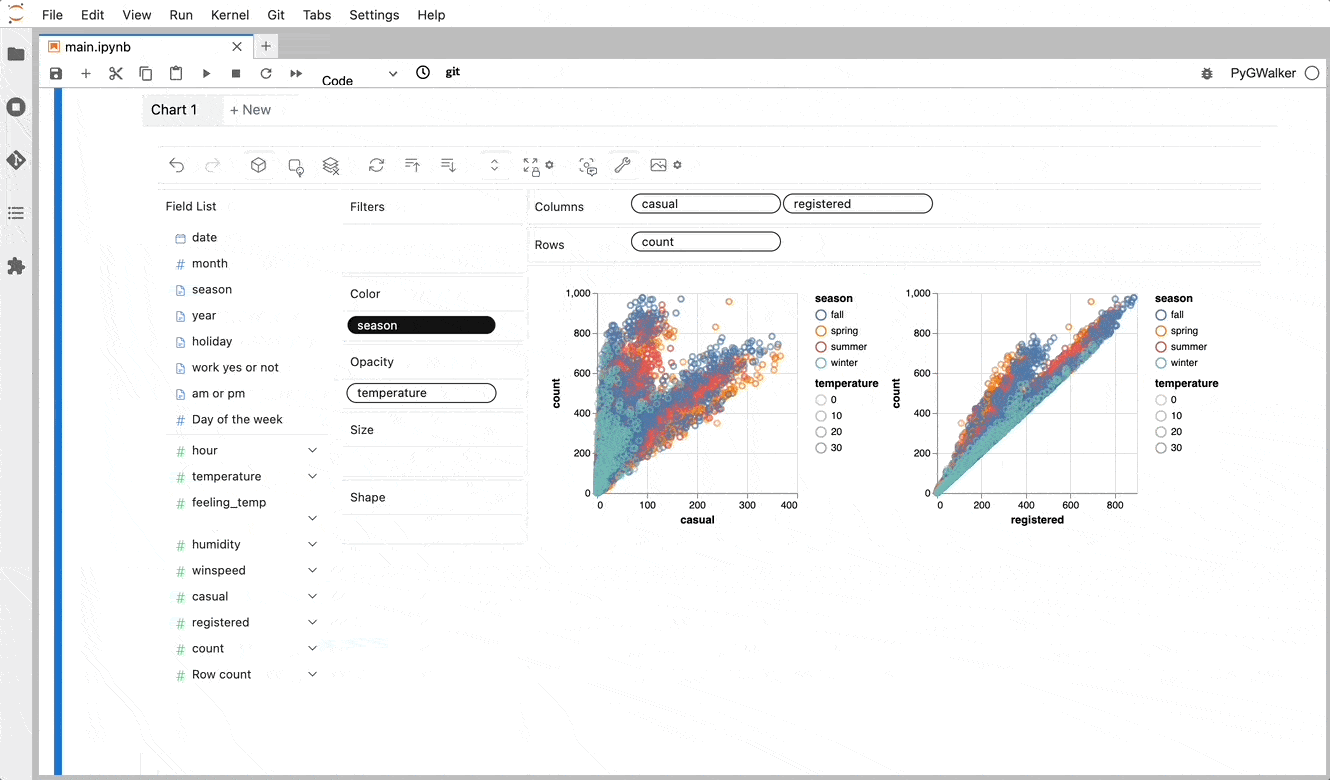
EDA is a crucial step in any Data Science project. For large datasets, EDA can be time-consuming.
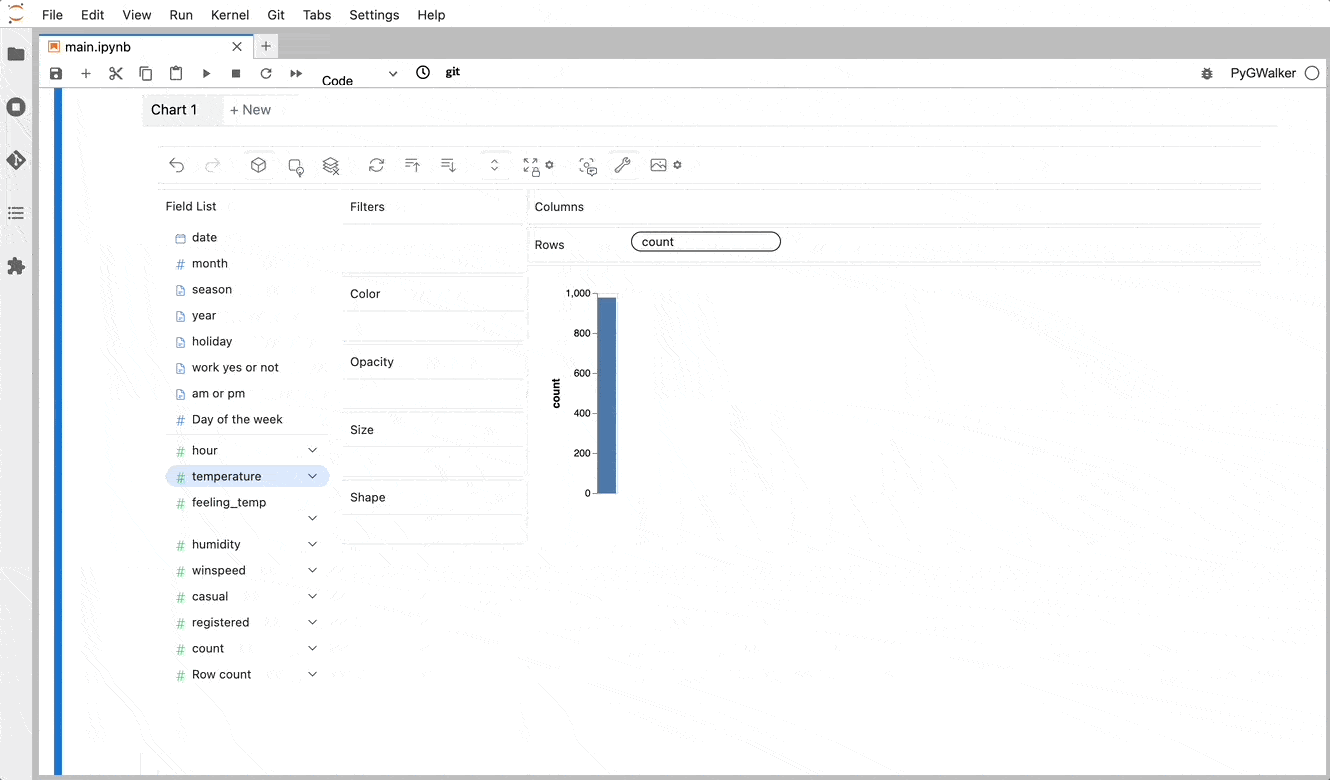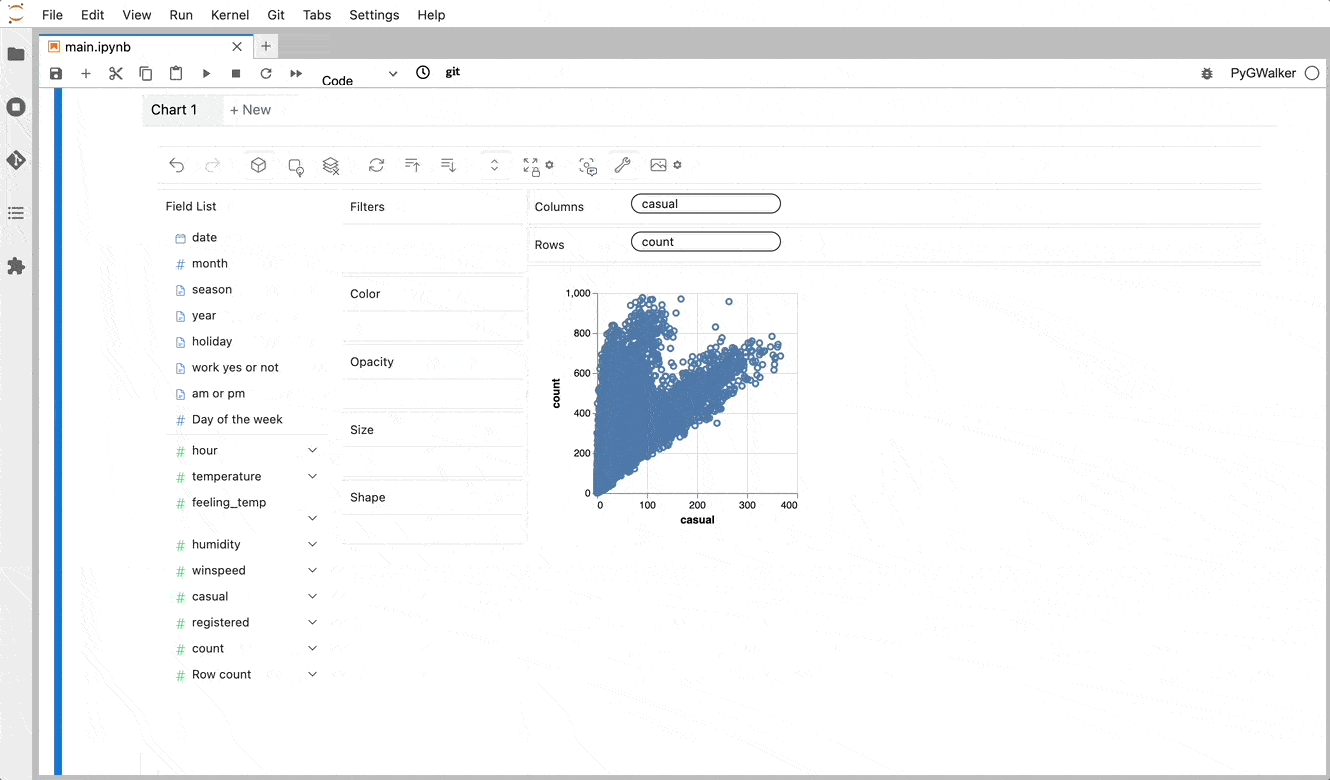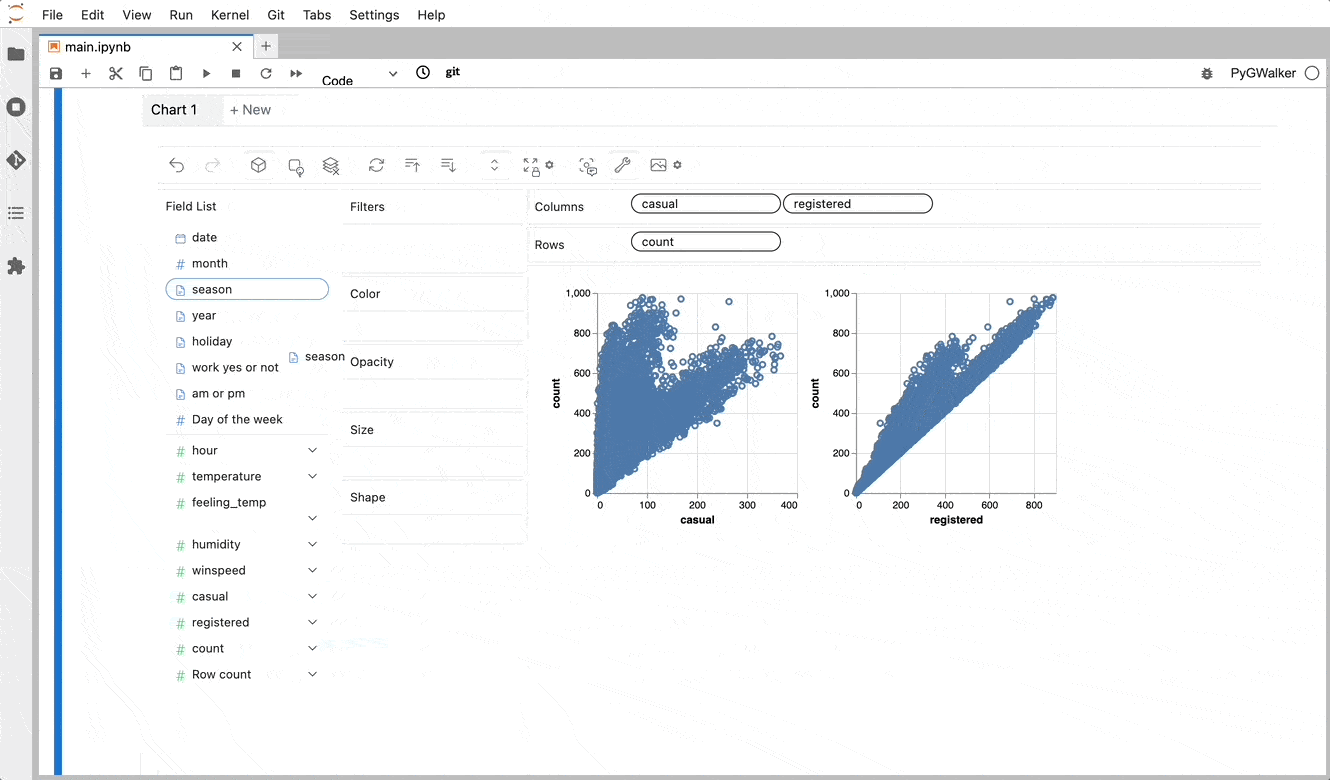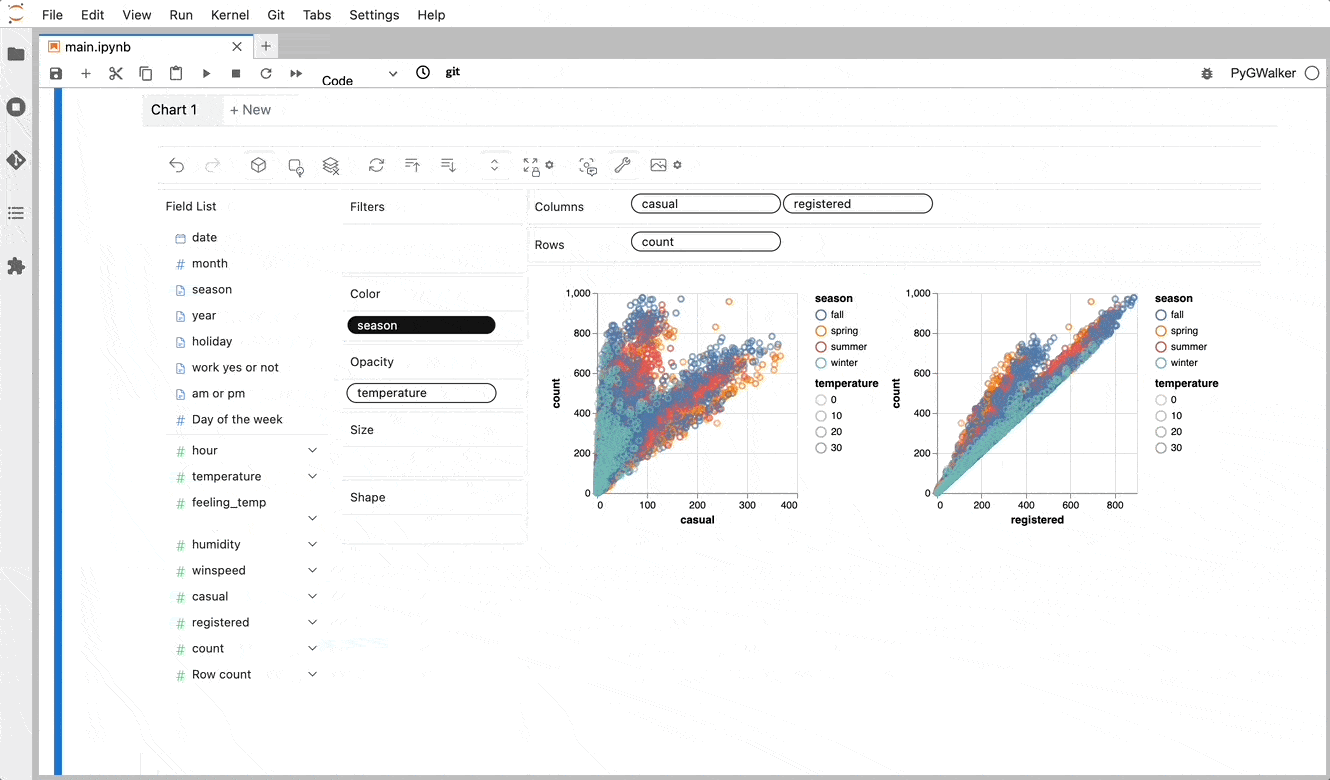
PyGWalker simplifies the process of creating visualizations by allowing users to drag and drop variables to create charts without writing much code.
You can use PyGWalker without changing your existing workflow. For example, you can call up PyGWalker with the Dataframe loaded in this way:
import pygwalker as pyg
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("https://kanaries-app.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/public-datasets/bike_sharing_dc.csv", parse_dates=['date'])
df.head(10)Output:
date month season hour year holiday temperature feeling_temp \
0 2011-01-01 1 winter 0 2011 no 3.28 3.0014
1 2011-01-01 1 winter 1 2011 no 2.34 1.9982
2 2011-01-01 1 winter 2 2011 no 2.34 1.9982
3 2011-01-01 1 winter 3 2011 no 3.28 3.0014
4 2011-01-01 1 winter 4 2011 no 3.28 3.0014
humidity winspeed casual registered count work yes or not am or pm \
0 81.0 0.0 3 13 16 0 am
1 80.0 0.0 8 32 40 0 am
2 80.0 0.0 5 27 32 0 am
3 75.0 0.0 3 10 13 0 am
4 75.0 0.0 0 1 1 0 am
Day of the week
0 6
1 6
2 6
3 6
4 6 And then just walk around!