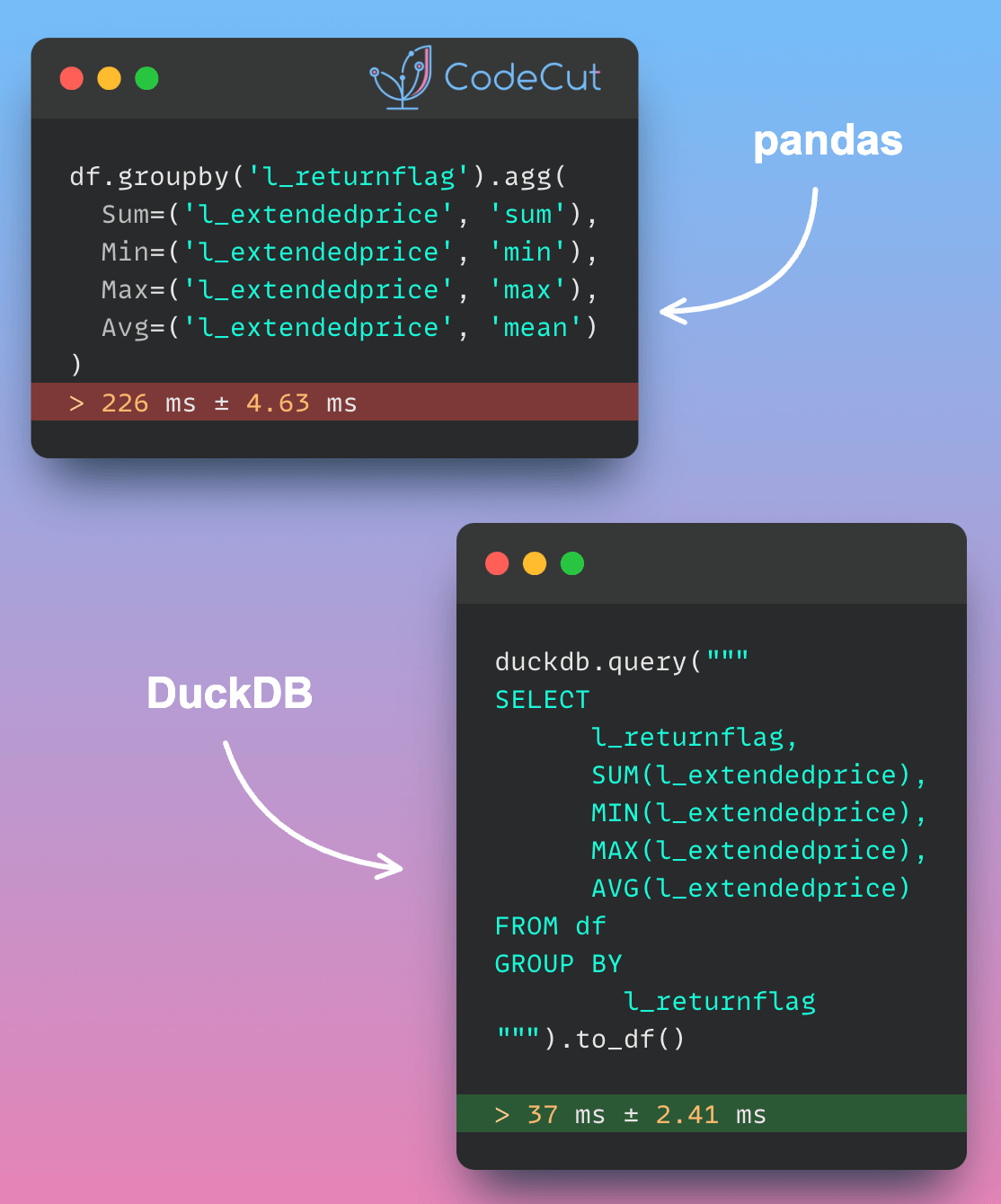
For complex aggregations, Pandas repeatedly scans the full dataset to compute metrics like averages and sums. This approach becomes increasingly inefficient as aggregation complexity or data volume grows.
DuckDB reads only necessary data columns and processes information in chunks. This approach makes it much faster for complex calculations, especially with large datasets
In the code below, aggregating data using DuckDB is nearly 6 times faster compared to aggregating with pandas.
import pandas as pd
import duckdb
df = pd.read_parquet("lineitemsf1.snappy.parquet")%%timeit
df.groupby('l_returnflag').agg(
Sum=('l_extendedprice', 'sum'),
Min=('l_extendedprice', 'min'),
Max=('l_extendedprice', 'max'),
Avg=('l_extendedprice', 'mean')
)Output:
226 ms ± 4.63 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)%%timeit
duckdb.query("""
SELECT
l_returnflag,
SUM(l_extendedprice),
MIN(l_extendedprice),
MAX(l_extendedprice),
AVG(l_extendedprice)
FROM df
GROUP BY
l_returnflag
""").to_df()Output:
37 ms ± 2.41 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)