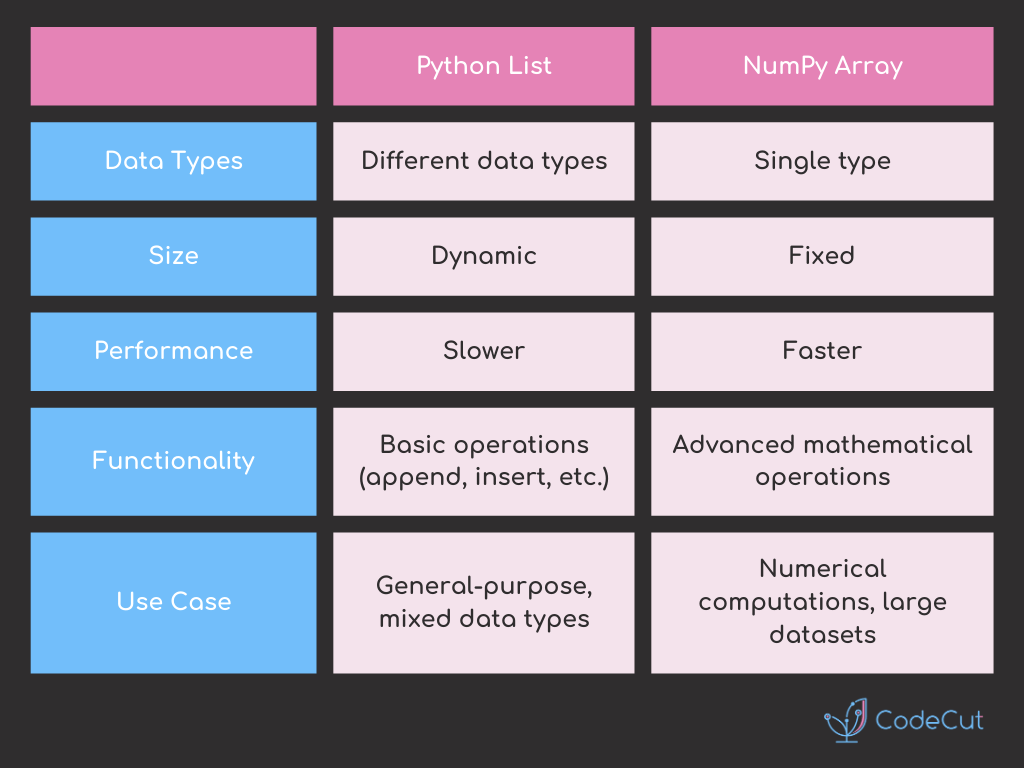
Python offers two popular data structures for storing collections: built-in lists and NumPy arrays. Understanding their differences is crucial for efficient programming.
Key Differences:
Data Types
- Lists: Can mix types
mixed_list = [1, "hello", 3.14, True]- NumPy: Homogeneous
import numpy as np
homogeneous_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])Performance
- Lists: Slower for numerical operations
list_data = list(range(1000000))
%time squared_list = [x**2 for x in list_data]
# Output: CPU times: user 26.4 ms, sys: 7.96 ms, total: 34.3 ms- NumPy: Optimized for numerical computations
np_data = np.arange(1000000)
%time squared_np = np_data**2
# Output: CPU times: user 9 ms, sys: 830 μs, total: 9.83 msFunctionality
- Lists: Basic operations
lst = [1, 2, 3]
lst.append(4)
lst.insert(0, 0)
print(lst) # Output: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]- NumPy: Advanced mathematical operations and broadcasting
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(np.sin(arr)) # Output: [0.84147098 0.90929743 0.14112001]
print(arr + np.array([10, 20, 30])) # Output: [11 22 33]Dimensionality
- Lists: Nesting for multi-dimensions
nested_list = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
print(nested_list[1][0]) # Output: 3- NumPy: Native support for multi-dimensional arrays
matrix = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(matrix.shape) # Output: (3, 2)
print(matrix[:, 1]) # Output: [2 4 6]When to Use Python Lists:
- Storing mixed data types
- Frequently changing collection size
- Working with small to medium-sized data
- General-purpose programming
Example:
user_data = [
{"name": "Alice", "age": 30, "active": True},
{"name": "Bob", "age": 25, "active": False}
]When to Use NumPy Arrays:
- Large numerical datasets
- Scientific computing and data analysis
- Need for advanced mathematical operations
- Working with multi-dimensional data
Example:
import numpy as np
data = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
mean = np.mean(data)
std_dev = np.std(data)
print(f"Mean: {mean}, Standard Deviation: {std_dev}")