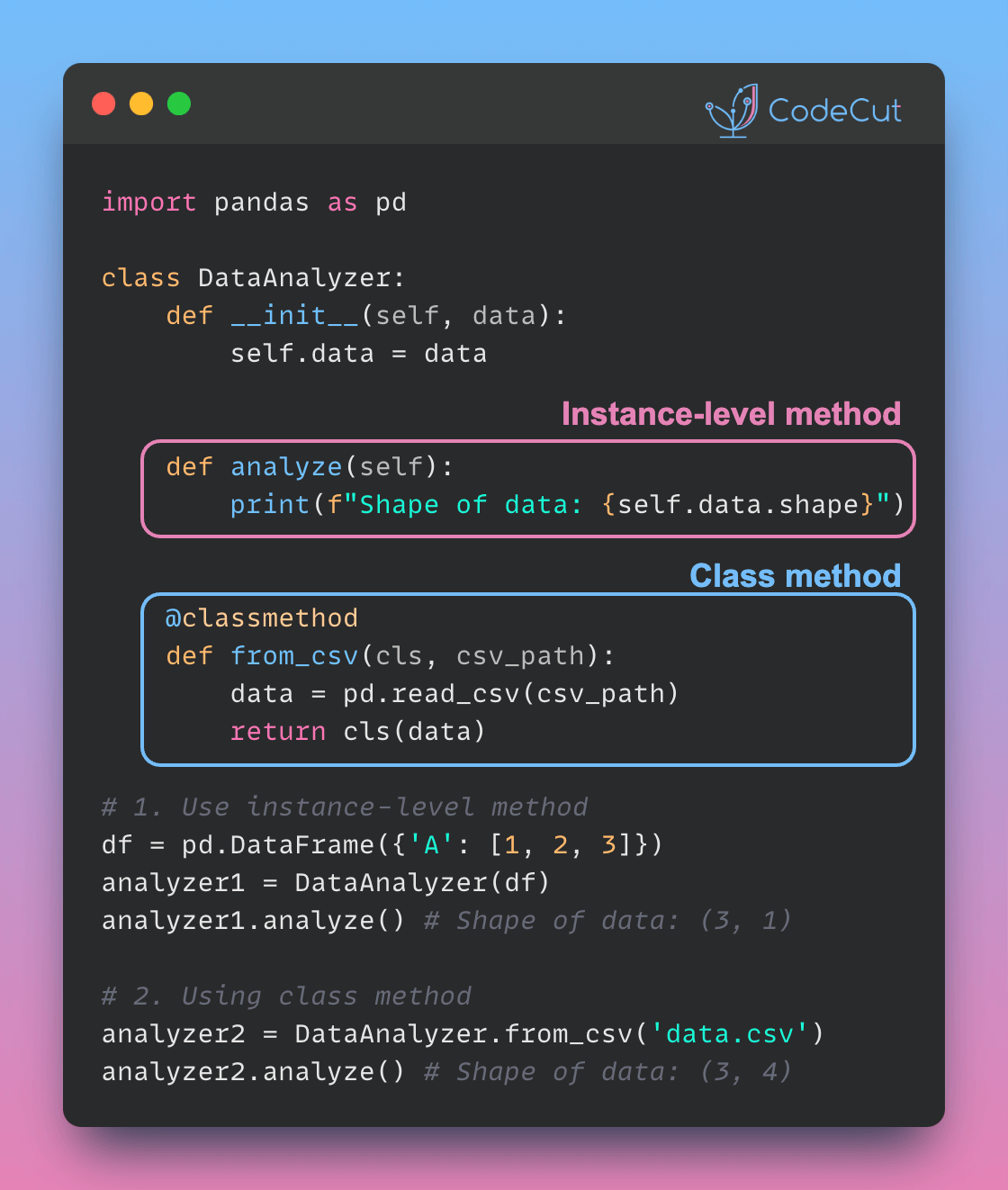
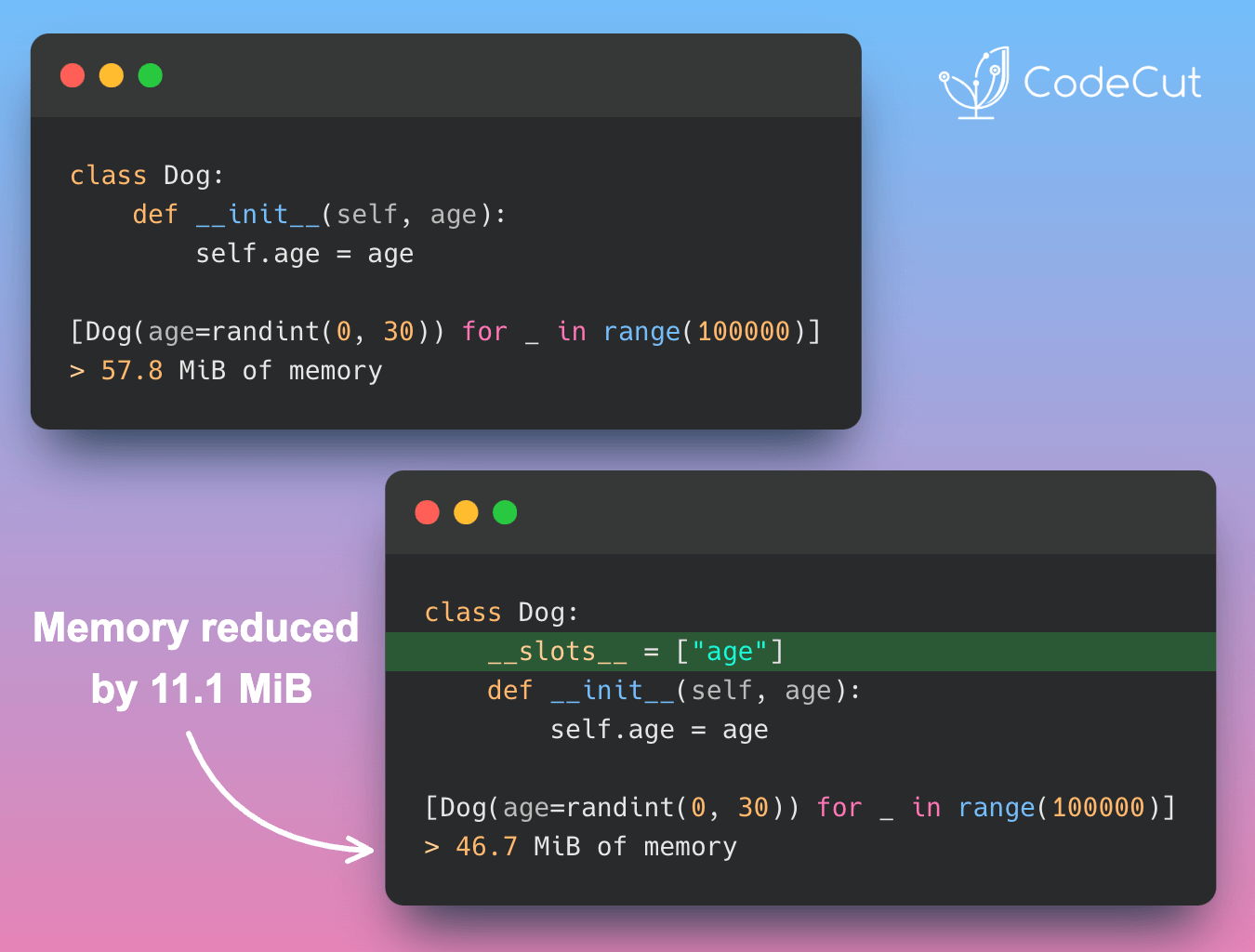
Motivation
Managing nested structures manually with dictionaries or objects can quickly become error-prone and increase code complexity. This often makes the code harder to maintain and debug.
For example, consider the following structure:
# Example of managing nested structures manually
person_data = {
"name": "Alice",
"address": {"street": "123 Maple St", "city": "Springfield", "zip": "12345"},
"contacts": {"email": "alice@example.com", "phone": "555-1234"},
}
# Accessing nested data
street = person_data["address"]["street"]
email = person_data["contacts"]["email"]
print(f"Street: {street}, Email: {email}")Output:
Street: 123 Maple St, Email: alice@example.comHere, accessing nested fields such as street and email involves repeatedly indexing into dictionaries. This approach can lead to runtime errors if a key is missing or mistyped, and the structure becomes harder to manage as it grows.
Introduction to the dataclasses Module
The Python dataclasses module, introduced in Python 3.7, provides a simple and declarative way to define structured data objects. It eliminates the need for manually writing boilerplate code like __init__ methods for classes. To use it, you can install Python 3.7 or later and directly import it into your project.
In this post, we will explore how dataclasses can simplify nested structures.
Simplify Nested Structures
The dataclasses module allows you to define hierarchical structures in a clean, type-safe, and declarative way. Let’s illustrate this by reconstructing the nested structure example using dataclasses.
from dataclasses import dataclass
# Define nested data classes
@dataclass
class Address:
street: str
city: str
zip: str
@dataclass
class Contacts:
email: str
phone: str
@dataclass
class Person:
name: str
address: Address
contacts: Contacts
# Create and use nested data classes
person = Person(
name="Alice",
address=Address(street="123 Maple St", city="Springfield", zip="12345"),
contacts=Contacts(email="alice@example.com", phone="555-1234"),
)
print(f"Street: {person.address.street}, Email: {person.contacts.email}")
Output:
Street: 123 Maple St, Email: alice@example.com
Using dataclasses provides the following benefits:
dataclassautomatically generates the__init__method, making it easier to construct objects.- Nested structures like
AddressandContactsare more intuitive and type-safe. - Accessing data like
person.address.streetis cleaner and less error-prone.
Conclusion
The dataclasses module in Python is a powerful tool for managing structured and hierarchical data. It improves readability, reduces boilerplate code, and ensures type safety, making it an excellent choice for handling nested structures. By adopting dataclasses, you can simplify your code and focus on solving the actual problem.