🤝 COLLABORATION
Build Safer APIs with Buf – Free Workshop
Building APIs is simple. Scaling them across teams and systems isn’t. Ensuring consistency, compatibility, and reliability quickly becomes a challenge as projects grow.
Buf provides a toolkit that makes working with Protocol Buffers faster, safer, and more consistent.
Join Buf for a live, one-hour workshop on building safer, more consistent APIs.
When: Nov 19, 2025 • 9 AM PDT | 12 PM EDT | 5 PM BST
What you’ll learn:
- How Protobuf makes API development safer and simpler
- API design best practices for real-world systems
- How to extend Protobuf to data pipelines and streaming systems
📅 Today’s Picks
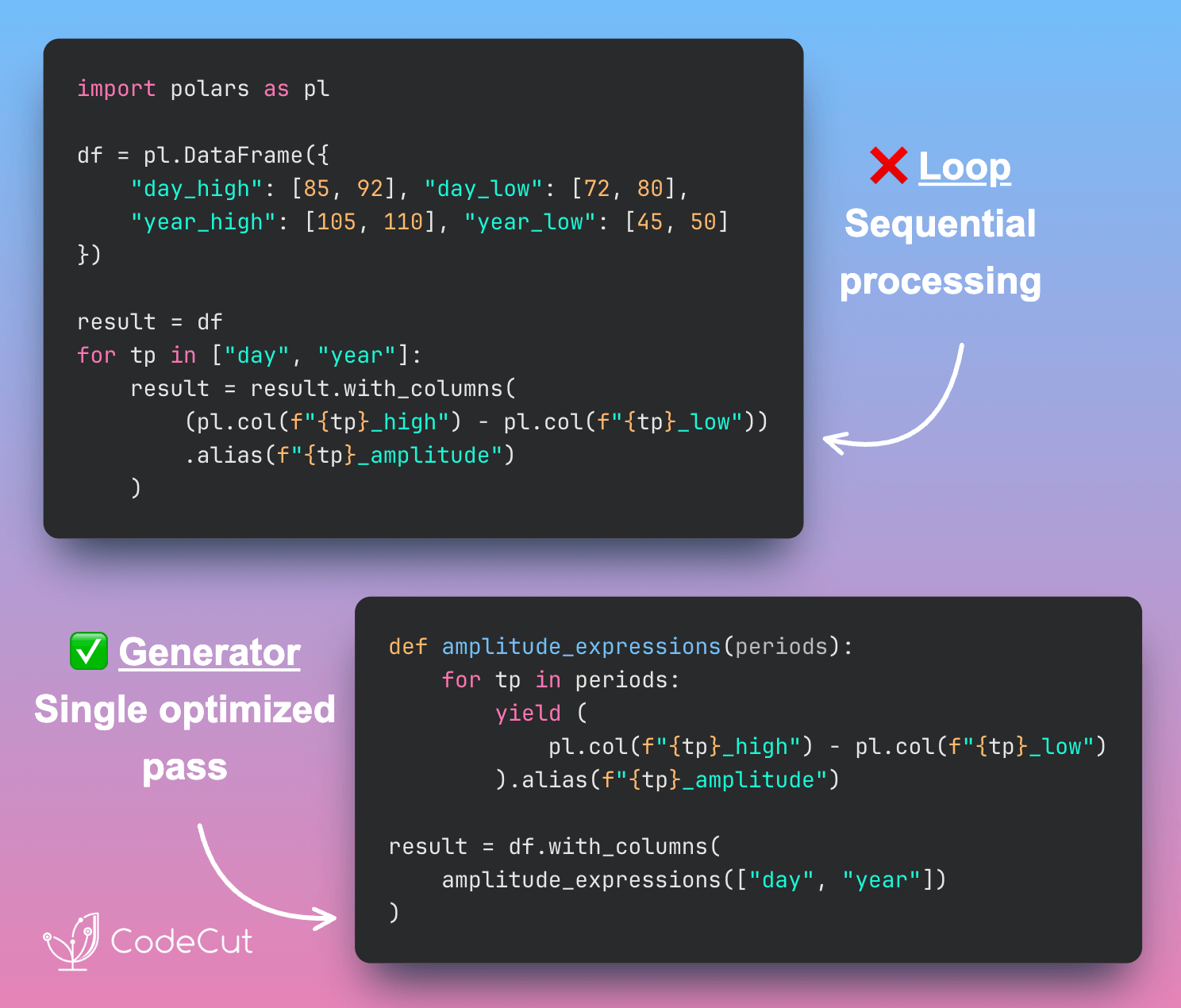
Faster Polars Queries with Programmatic Expressions
Problem
When you want to use for loops to apply similar transformations, each Polars with_columns() call processes sequentially.
This prevents the optimizer from seeing the full computation plan.
Solution
Instead, generate all Polars expressions programmatically before applying them together.
This enables Polars to:
- See the complete computation plan upfront
- Optimize across all expressions simultaneously
- Parallelize operations across CPU cores
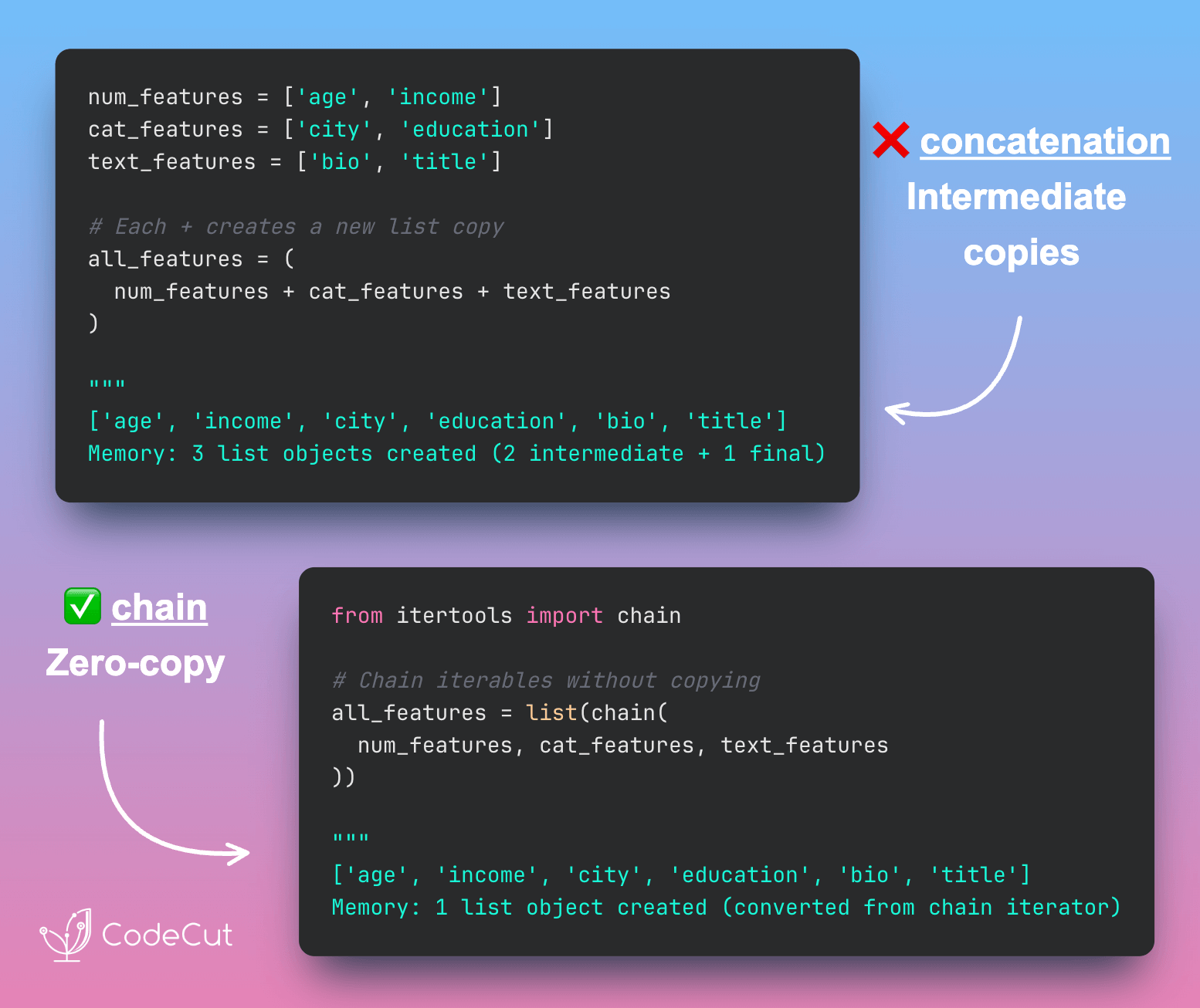
itertools.chain: Merge Lists Without Intermediate Copies
Problem
Standard list merging with extend() or concatenation creates intermediate copies.
This memory overhead becomes significant when processing large lists.
Solution
itertools.chain() lazily merges multiple iterables without creating intermediate lists.
☕️ Weekly Finds
fiftyone [ML] – Open-source tool for building high-quality datasets and computer vision models
llama-stack [LLM] – Composable building blocks to build Llama Apps with unified API for inference, RAG, agents, and more
grip [Python Utils] – Preview GitHub README.md files locally before committing them using GitHub’s markdown API
Looking for a specific tool? Explore 70+ Python tools →
Stay Current with CodeCut
Actionable Python tips, curated for busy data pros. Skim in under 2 minutes, three times a week.