📅 Today’s Picks
Build Fast Recommendations with Annoy’s Memory-Mapped Indexes
Problem
sklearn loads all your item vectors into memory and compares your search vector against every single item in your dataset.
This can take seconds or minutes when you have millions of items.
Solution
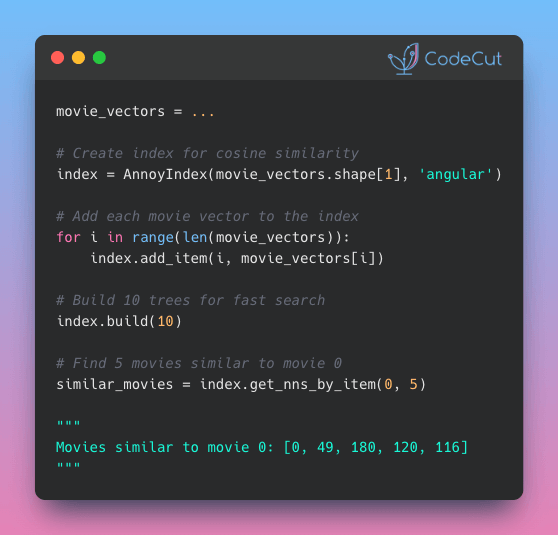
Annoy (Approximate Nearest Neighbors Oh Yeah), built by Spotify, speeds up similarity search by organizing your vectors into a searchable tree structure.
How it works:
- Pre-builds indexes with “build(n_trees)”, creating multiple trees by recursively splitting your vector space with random hyperplanes
- Traverses tree splits to find the n nearest neighbors using “get_nns_by_item(i, n)”
- Checks only items in the final region instead of scanning everything
As a result, you can query millions of items in milliseconds instead of seconds.
Build Reliable DataFrame Tests with assert_frame_equal
Problem
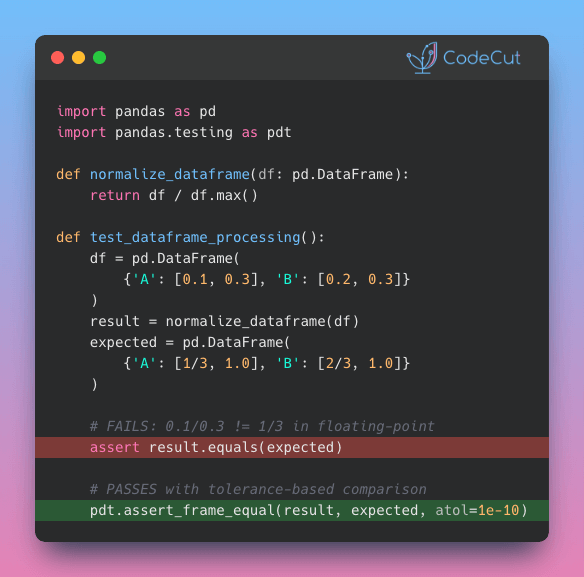
Testing numerical code with regular assertions can lead to false failures from floating-point precision.
Your perfectly correct function fails tests because 0.1 + 0.2 doesn’t exactly equal 0.3 in computer arithmetic.
Solution
Use numpy.testing and pandas.testing utilities for robust numerical comparisons.
Key approaches:
- assert_array_almost_equal for NumPy arrays with decimal precision control
- pd.testing.assert_frame_equal for DataFrame comparisons with tolerance
- Handle floating-point arithmetic limitations properly
- Get reliable test results for numerical data processing
Professional data science requires proper numerical testing methods.
☕️ Weekly Finds
sympy [Python Utils] – A computer algebra system written in pure Python for symbolic mathematics
qdrant [LLM] – High-performance, massive-scale Vector Database and Vector Search Engine for the next generation of AI
mindsdb [ML] – Federated query engine for AI – connect to hundreds of data sources and generate intelligent responses using built-in agents
Looking for a specific tool? Explore 70+ Python tools →
Stay Current with CodeCut
Actionable Python tips, curated for busy data pros. Skim in under 2 minutes, three times a week.