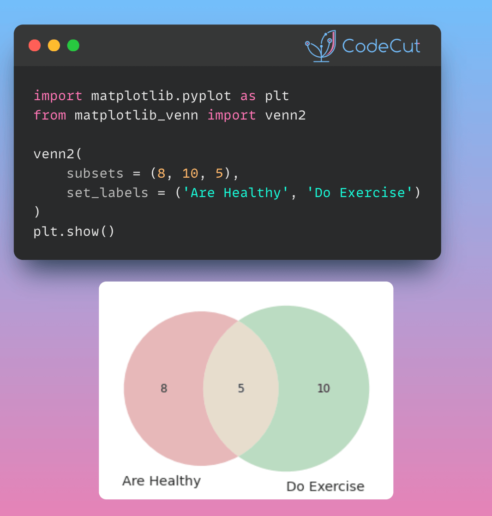
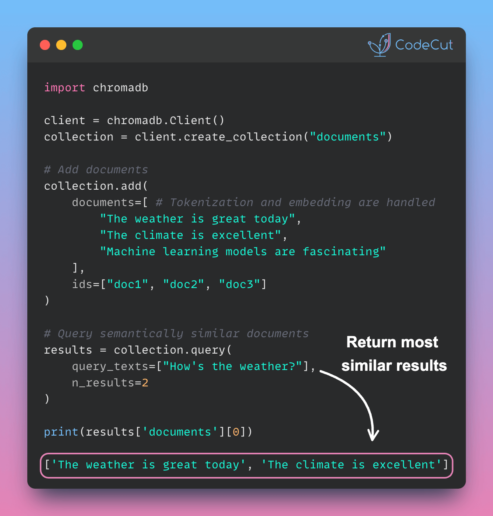
Handling geographic data in Python can be complex and cumbersome without the right tools. In this article, we will explore the challenges of working with geographic data manually and introduce a powerful library that simplifies the process: GeoPandas.
The Challenges of Manual Geographic Data Handling
When working with geographic data without specialized tools, you need to manually handle coordinates and spatial operations. This can lead to complex and error-prone code. Here’s an example of calculating the area and perimeter of two polygons using manual handling:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Complex manual handling of polygon coordinates
df = pd.DataFrame({
'name': ['Area1', 'Area2'],
'coordinates': [
[(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1)],
[(2, 0), (3, 0), (3, 1), (2, 1)]
]
})
# Calculate area
def calculate_polygon_area(coordinates):
x_coords = [point[0] for point in coordinates]
y_coords = [point[1] for point in coordinates]
# Add first point to end to close the polygon
x_shifted = x_coords[1:] + x_coords[:1]
y_shifted = y_coords[1:] + y_coords[:1]
# Calculate using shoelace formula
first_sum = sum(x * y for x, y in zip(x_coords, y_shifted))
second_sum = sum(x * y for x, y in zip(x_shifted, y_coords))
area = 0.5 * abs(first_sum - second_sum)
return area
df['area'] = df['coordinates'].apply(calculate_polygon_area)
df['area']0 0.5
1 1.0
Name: area, dtype: float64# Calculate parameter
def calculate_perimeter(coordinates):
# Add first point to end to close the polygon if not already closed
if coordinates[0] != coordinates[-1]:
coordinates = coordinates + [coordinates[0]]
# Calculate distance between consecutive points
distances = []
for i in range(len(coordinates)-1):
point1 = coordinates[i]
point2 = coordinates[i+1]
# Euclidean distance formula
distance = np.sqrt((point2[0] - point1[0])**2 + (point2[1] - point1[1])**2)
distances.append(distance)
return sum(distances)
df['perimeter'] = df['coordinates'].apply(calculate_perimeter)
df['perimeter']Output:
0 3.414214
1 4.000000
Name: perimeter, dtype: float64Simplifying Geographic Data Handling with GeoPandas
GeoPandas is a powerful library that simplifies working with geographic data in Python. With GeoPandas, you can:
- Work with geometric objects (points, lines, polygons) directly in DataFrame-like structures
- Perform spatial operations (intersections, unions, buffers) easily
- Visualize geographic data with simple plotting commands
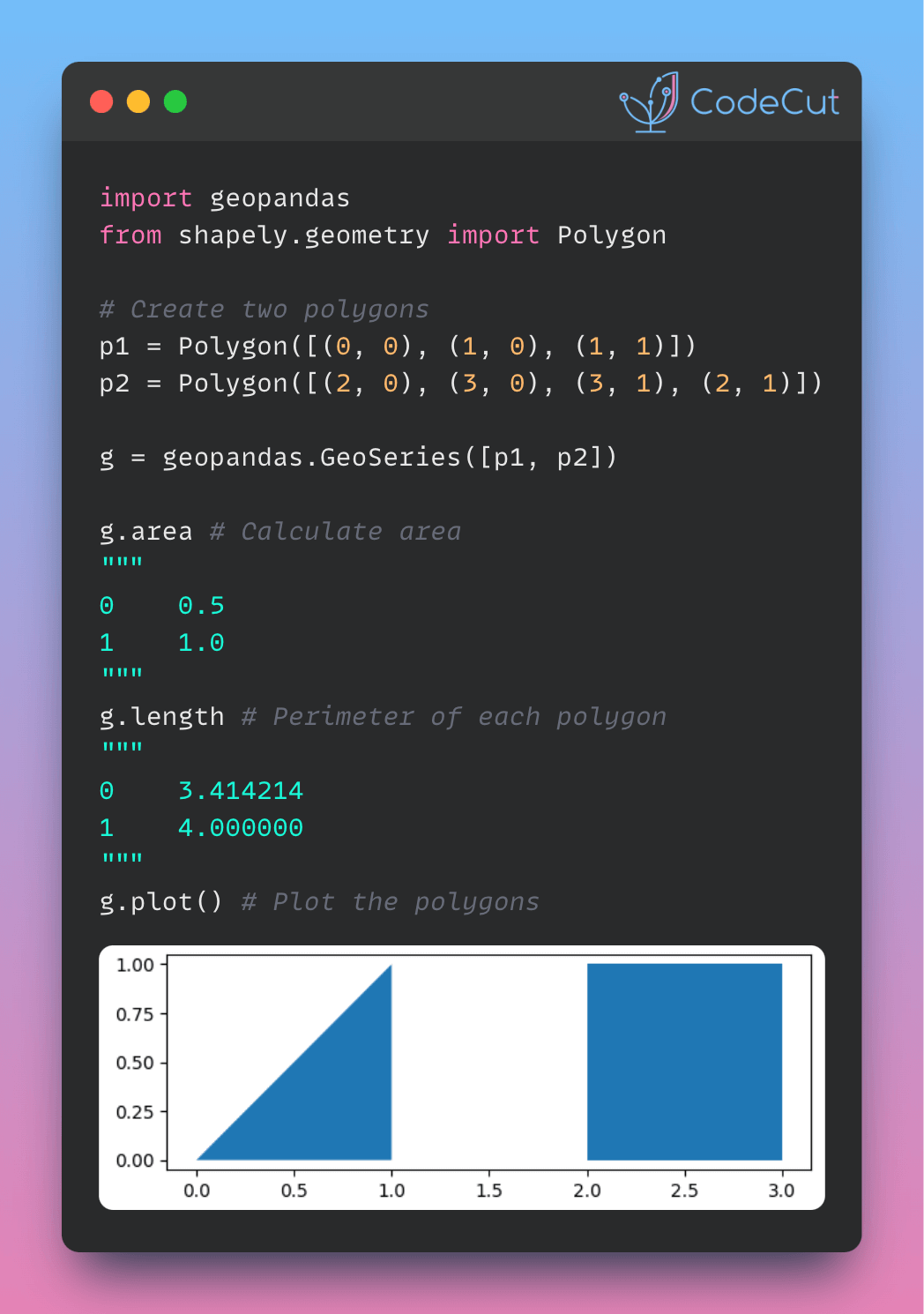
Here’s an example of using GeoPandas to calculate the area and perimeter of two polygons:
import geopandas
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
# Create two polygons
p1 = Polygon([(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1)])
p2 = Polygon([(2, 0), (3, 0), (3, 1), (2, 1)])
# Create a GeoSeries from the polygons
g = geopandas.GeoSeries([p1, p2])
# Calculate area
g.areaOutput:
0 0.5
1 1.0
dtype: float64# Perimeter of each polygon
g.lengthOutput:
0 3.414214
1 4.000000
dtype: float64g.plot()Output:

By using GeoPandas, you can significantly simplify your code and make working with geographic data more efficient and enjoyable.