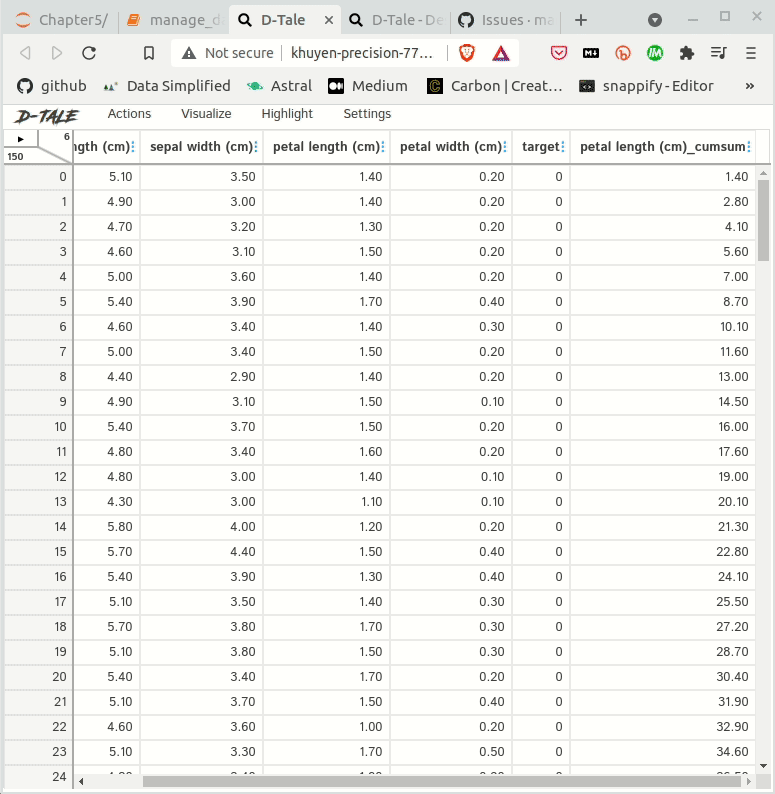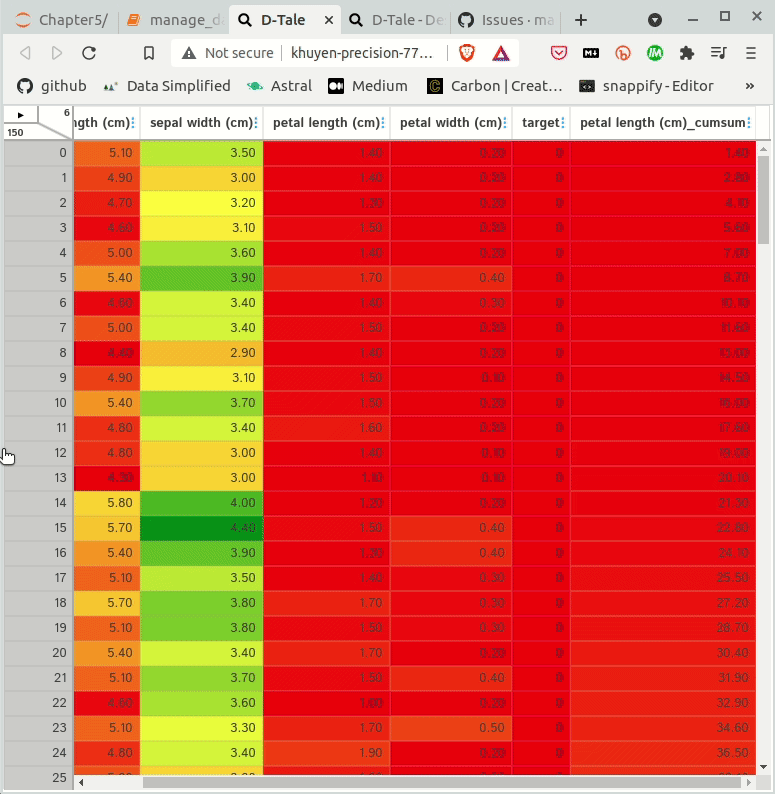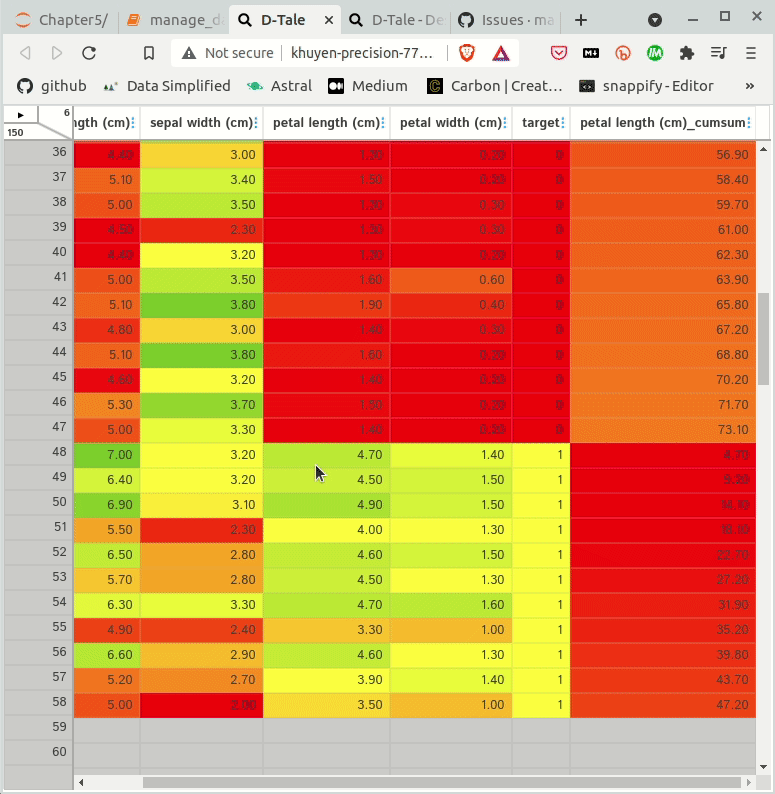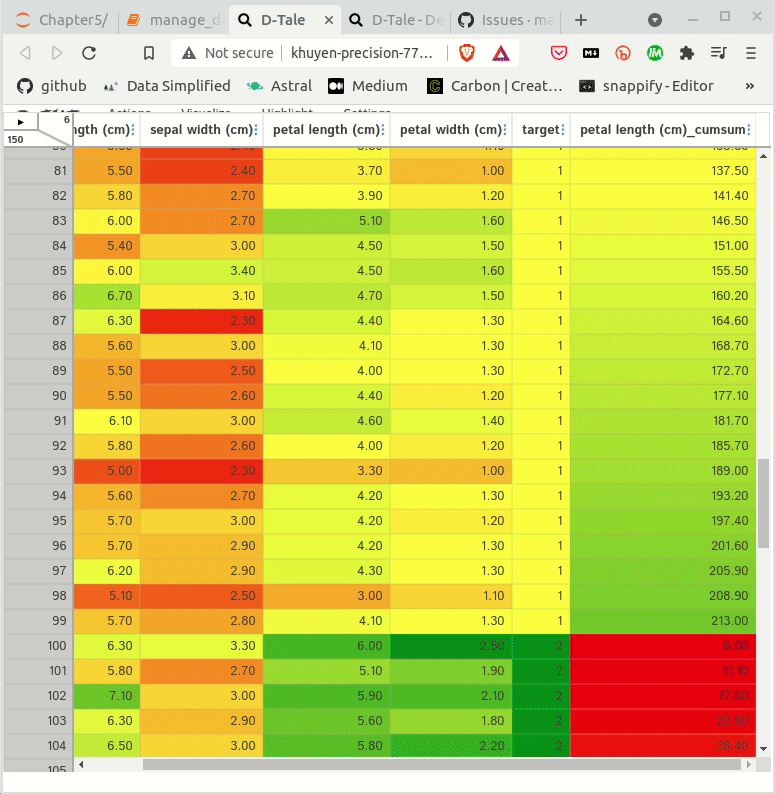
SQLPage: Generate Web UIs From SQL Queries
Motivation
Data scientists and analysts often need to build web interfaces to share their data and analyses, but most lack web development expertise. They end up either creating static reports or relying on web developers to build interactive dashboards.
Example:
# Traditional way: Need to learn Flask/FastAPI, HTML, CSS, JavaScript
from flask import Flask, render_template
import pandas as pd
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def show_websites():
# Need to handle database connection
# Need to create HTML templates
# Need to style the output
websites_df = pd.read_sql("""
SELECT name, url, type, description
FROM website
""", db_connection)
return render_template('websites.html', websites=websites_df.to_dict('records'))
Introduction to SQLPage
SQLPage is a tool that automatically builds web interfaces directly from SQL queries. It eliminates the need to write any traditional web programming code by providing pre-built components that render your data.
SQL-Based Web Interface
SQLPage solves the web interface problem by letting you:
Create web pages using only SQL queries
Automatically generate styled components
Handle interactive elements without JavaScript
Create a file named dashboard.sql:
— Create a list component with a title
SELECT
'list' as component,
'Popular websites' as title;
— Query data and specify how to display each item
SELECT
name as title,
url as link,
CASE type
WHEN 1 THEN 'blue'
ELSE 'red'
END as color,
description,
icon,
active
FROM website;
The SQL code above will generate:
A styled list component with a header
Each website is displayed as a list item with:
The name as a clickable title
Color-coded items based on type
Description and icon for each website
Active state indication
Conclusion
SQLPage enables data professionals to create interactive web interfaces using only SQL, making it easier to share data insights with stakeholders. Instead of learning multiple web technologies, analysts can leverage their SQL skills to build professional-looking web applications.
Link to SQLPage
Favorite
SQLPage: Generate Web UIs From SQL Queries Read More »