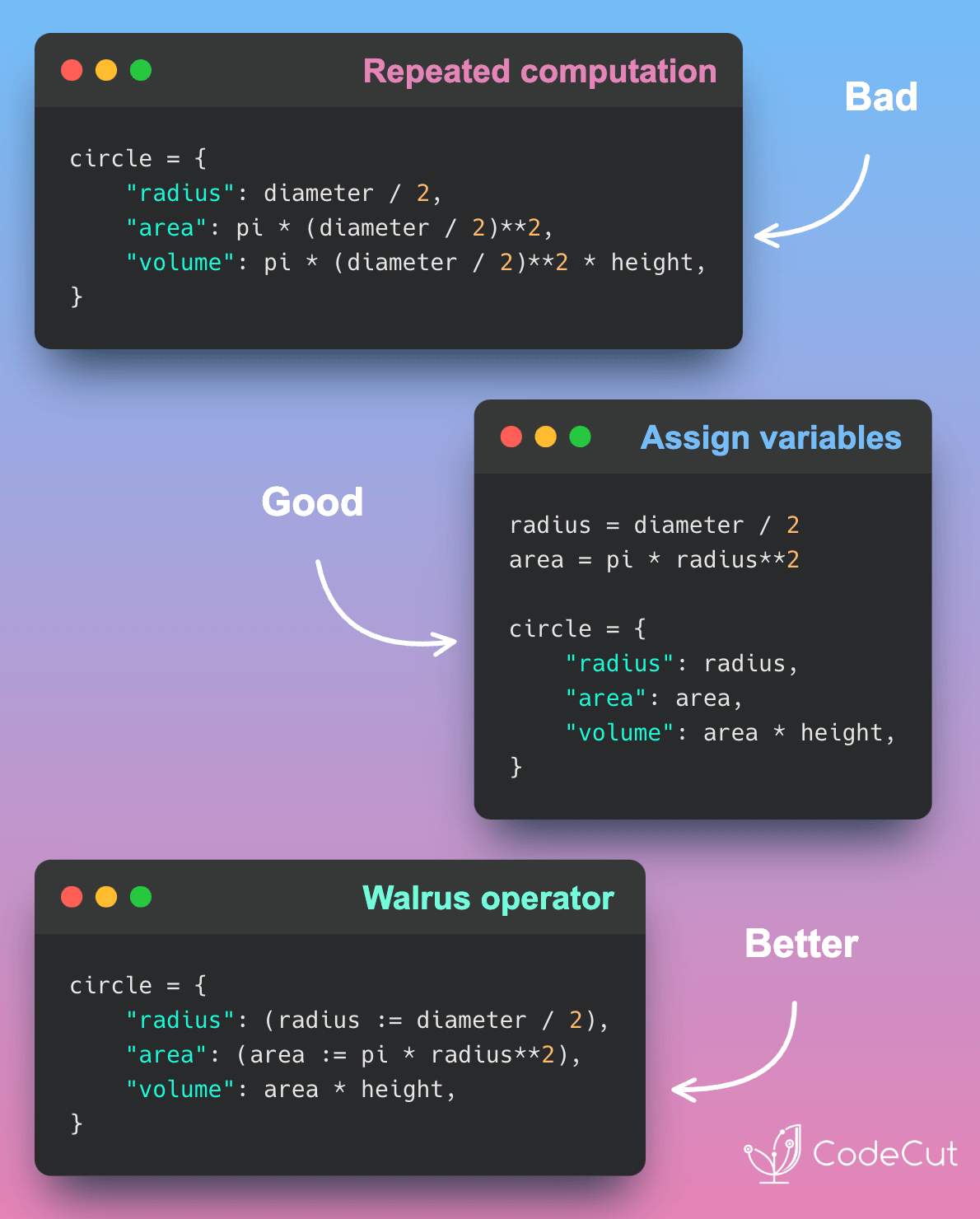
The walrus operator (:=) in Python 3.8+ allows you to assign a variable in an expression, making your code more readable and efficient. It’s useful in two main scenarios:
- Giving a meaningful name to a complex expression for better readability.
- Avoiding repeated computations by reusing a variable instead of recomputing the expression.
Let’s consider an example where we want to calculate the radius, area, and volume of a circle given its diameter and height:
from math import pi
diameter = 4
height = 2Without the walrus operator, we might compute the radius and area multiple times:
circle = {
"radius": diameter / 2, # computed twice
"area": pi * (diameter / 2)**2, # computed twice
"volume": pi * (diameter / 2)**2 * height,
}2.0To avoid repeated computations, we can assign the radius and area to variables before creating the dictionary:
radius = diameter / 2
area = pi * radius**2
circle = {
"radius": radius,
"area": area,
"volume": area * height,
}2.0To make the code more concise, we can use the walrus operator to assign the radius and area to variables while creating the dictionary.
circle = {
"radius": (radius := diameter / 2),
"area": (area := pi * radius**2),
"volume": area * height,
}After executing the code with the walrus operator, we can access the assigned variables:
print(radius)
print(area)2.0
12.566370614359172By using the walrus operator, we can simplify our code, reduce repeated computations, and improve readability.