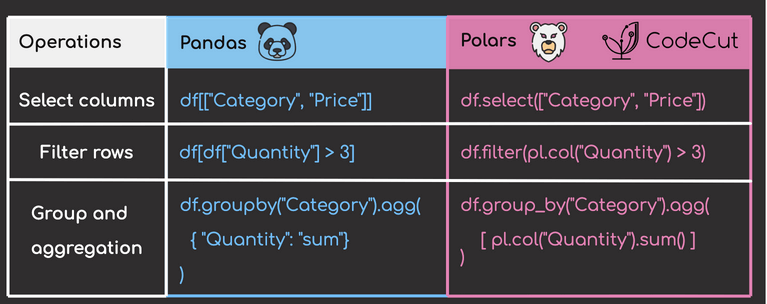
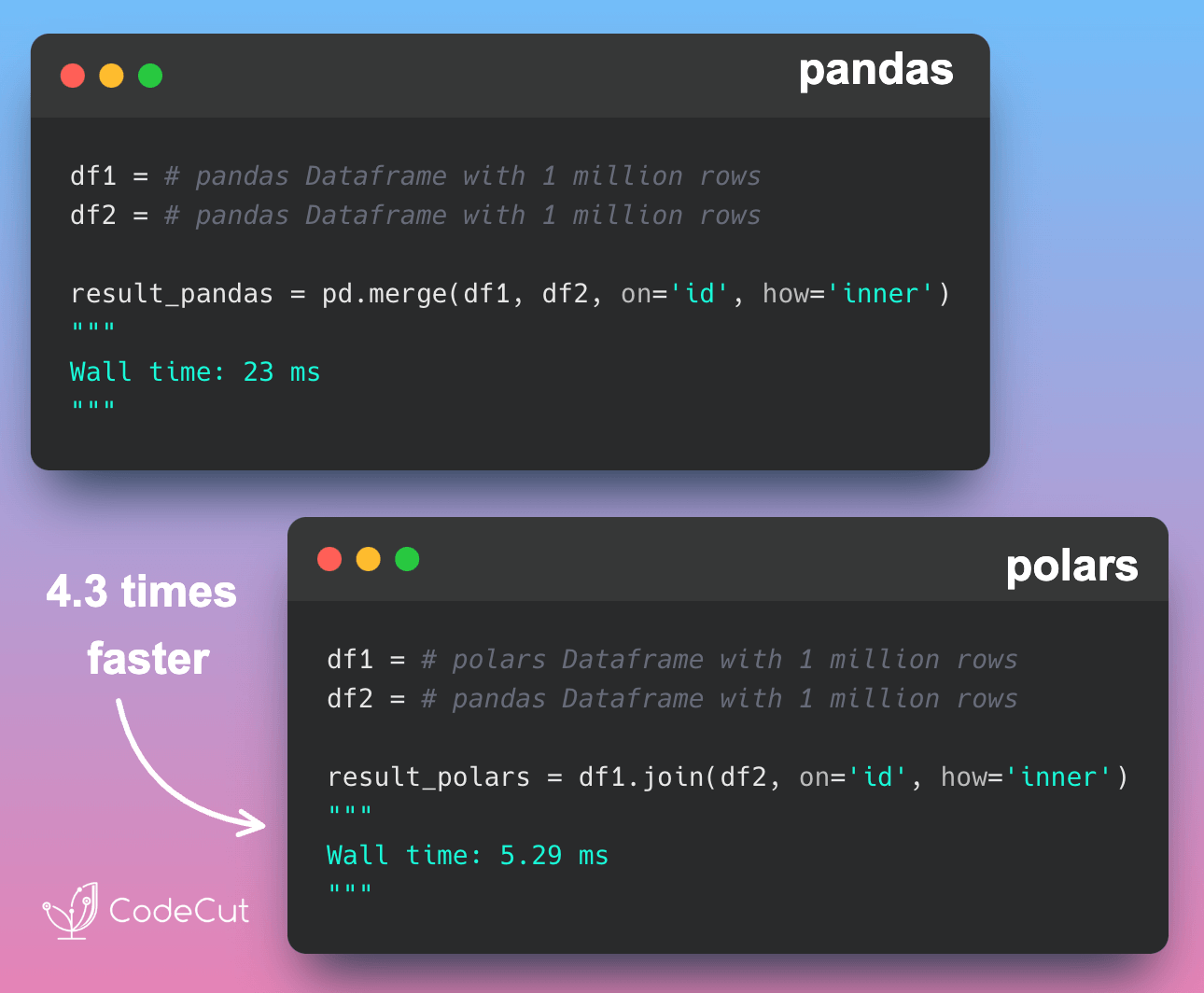
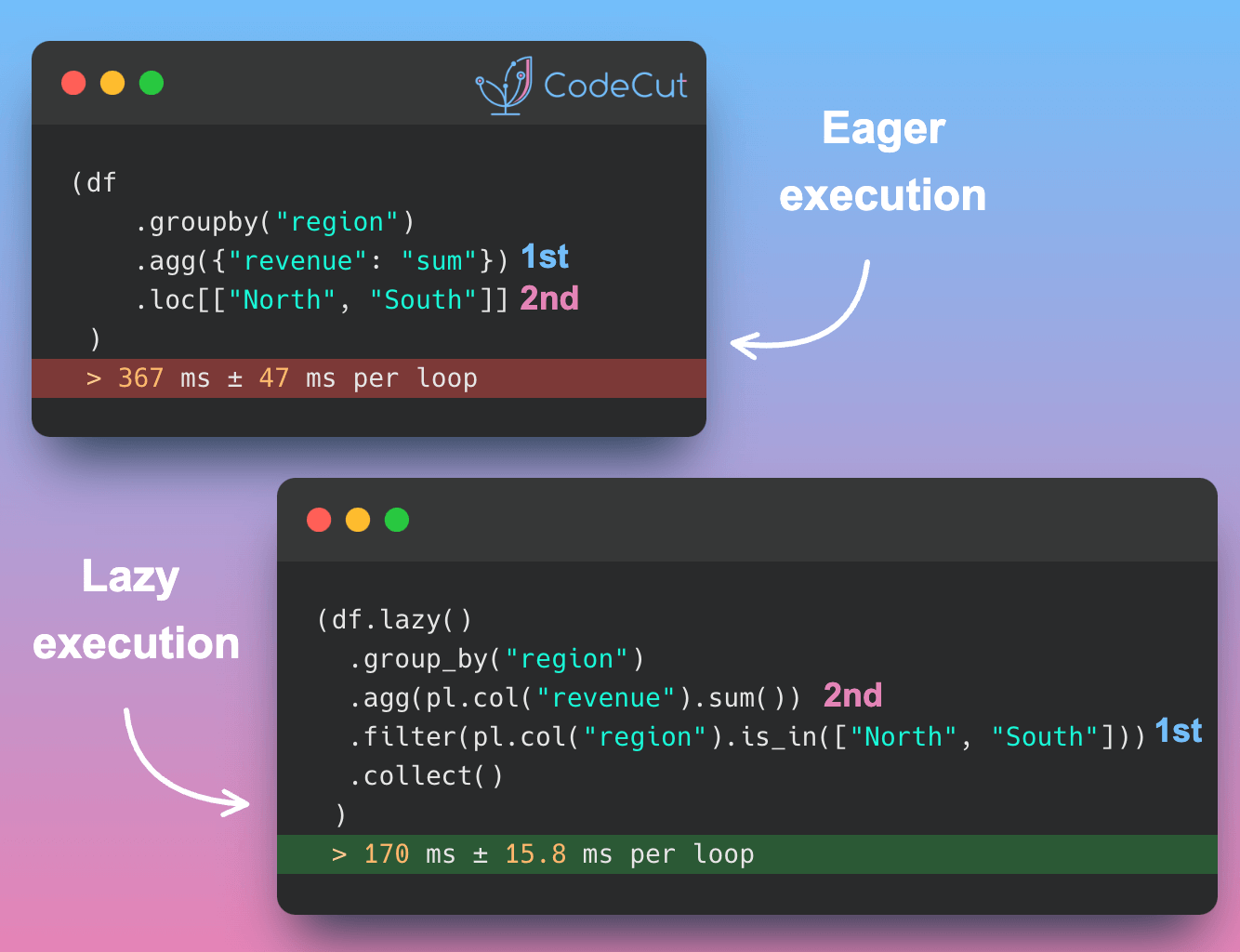
Both Pandas and Polars are robust data manipulation tools, but their syntaxes differ subtly. Let’s delve into how these libraries handle common data tasks.
To begin, we’ll create equivalent dataframes in both Pandas and Polars:
import pandas as pd
import polars as pl
# Sample data
sample_data = {
"Category": ["Electronics", "Clothing", "Electronics", "Clothing", "Electronics"],
"Quantity": [5, 2, 3, 10, 4],
"Price": [200, 30, 150, 20, 300],
}
# Dataframe creation
pandas_df = pd.DataFrame(sample_data)
polars_df = pl.DataFrame(sample_data)Key Operations Comparison
Column Selection
Pandas:
pandas_df[["Category", "Price"]]Polars:
polars_df.select(["Category", "Price"])Row Filtering
Pandas:
pandas_df[pandas_df["Quantity"] > 3]Polars:
polars_df.filter(pl.col("Quantity") > 3)Grouping and Aggregation
Pandas:
pandas_df.groupby("Category").agg(
{
"Quantity": "sum",
"Price": "mean",
}
)Polars:
polars_df.group_by("Category").agg(
[
pl.col("Quantity").sum(),
pl.col("Price").mean(),
]
)Polars tends to use more explicit, verb-based methods, while Pandas leverages more concise bracket notation.
The choice between Pandas and Polars often comes down to performance needs, library familiarity, and personal preference. Polars is known for its speed and efficiency. Pandas, on the other hand, has a larger ecosystem and is more widely adopted.
Want the full walkthrough?
Check out our in-depth guide on Polars vs Pandas: A Fast, Multi-Core Alternative for DataFrames.