Motivation
Managing default configurations across different environments or experiments is cumbersome, often requiring explicit specification of config options every time you run your application. Data scientists frequently need to switch between different database connections or model parameters, leading to repetitive command-line arguments.
Example of a pain point:
# Every time you run the script, you need to specify the database
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
db_type = sys.argv[1]
else:
raise ValueError("Please specify database type (mysql/postgresql)")
if db_type == "mysql":
db_config = {
"driver": "mysql",
"user": "root",
"pass": "secret"
}
elif db_type == "postgresql":
db_config = {
"driver": "postgresql",
"user": "postgres_user",
"pass": "drowssap"
}
Introduction to Hydra
Hydra is a configuration framework from Facebook Research that simplifies configuration management in complex applications. It provides a powerful way to manage configurations through YAML files and command-line overrides.
Installation:
pip install hydra-coreDefault Configurations
Hydra solves the default configuration problem by allowing you to:
- Set default configurations in a defaults list
- Override defaults through command line when needed
- Compose multiple default configurations hierarchically
Here’s an example of using Hydra’s default configurations:
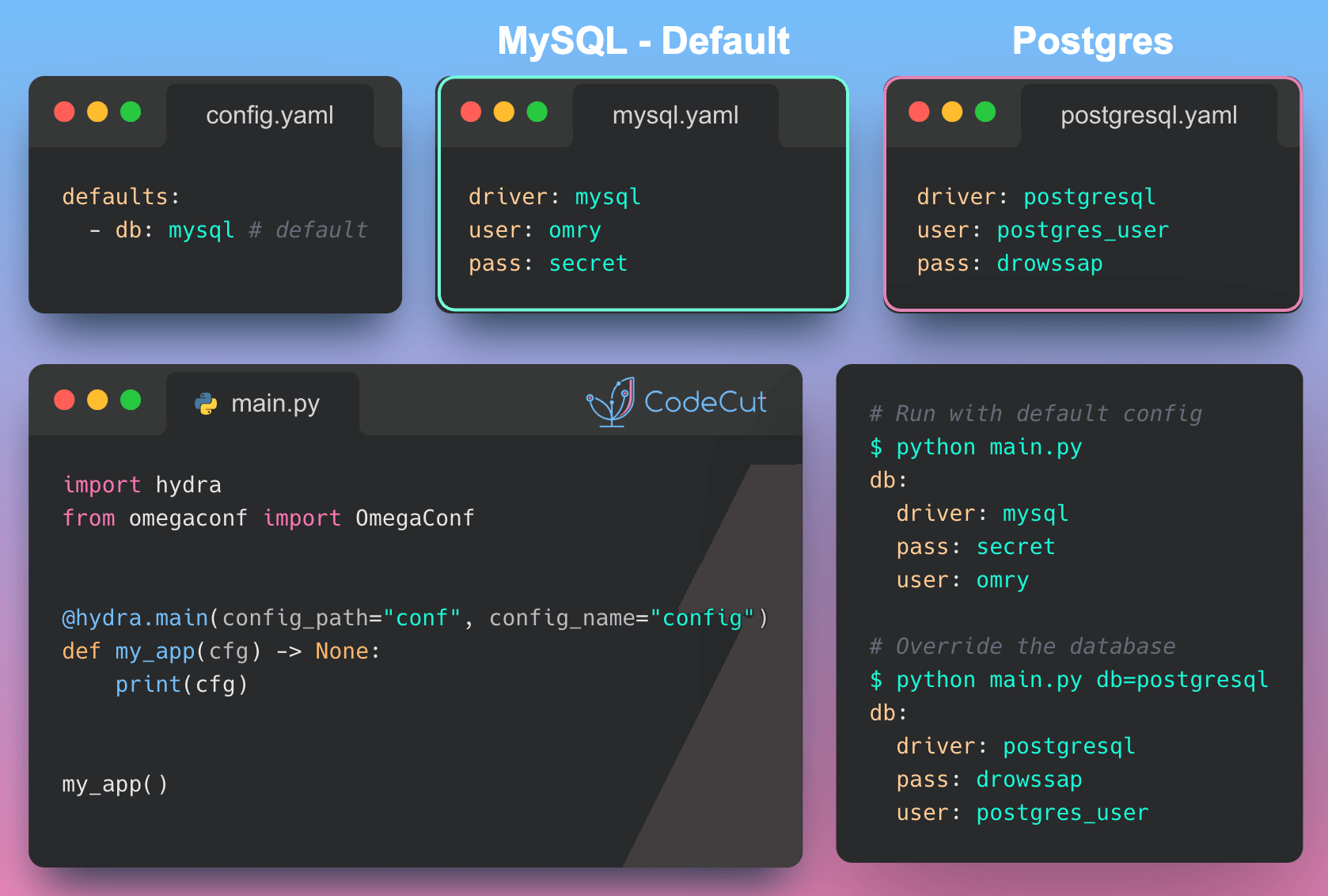
First, create the configuration files:
# conf/config.yaml
defaults:
- db: mysql # Set mysql as default database
# conf/db/mysql.yaml
driver: mysql
user: omry
pass: secret
# conf/db/postgresql.yaml
driver: postgresql
user: postgres_user
pass: drowssap
Create the Python application:
# my_app.py
import hydra
from omegaconf import DictConfig, OmegaConf
@hydra.main(version_base=None, config_path="conf", config_name="config")
def my_app(cfg: DictConfig) -> None:
print(OmegaConf.to_yaml(cfg))
if __name__ == "__main__":
my_app()
Running the application with default config:
python my_app.py
Output:
db:
driver: mysql
pass: secret
user: omry
Override the default database:
python my_app.py db=postgresql
Output:
db:
driver: postgresql
pass: drowssap
user: postgres_userConclusion
Hydra offers a robust solution for managing configurations in data science projects. Key features include:
- Command-line configuration override
- Composition of configurations from multiple sources
For a detailed overview, see the article “Stop Hard Coding in a Data Science Project – Use Config Files Instead”.