Newsletter #291: Docling: Turn DOCX Reviewer Feedback into Structured Data
Grab your coffee. Here are this week’s highlights.
📅 Today’s Picks
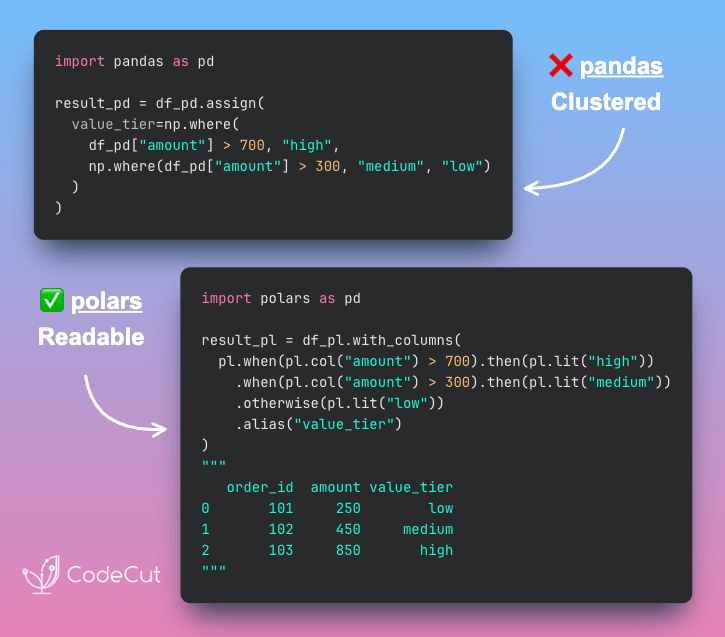
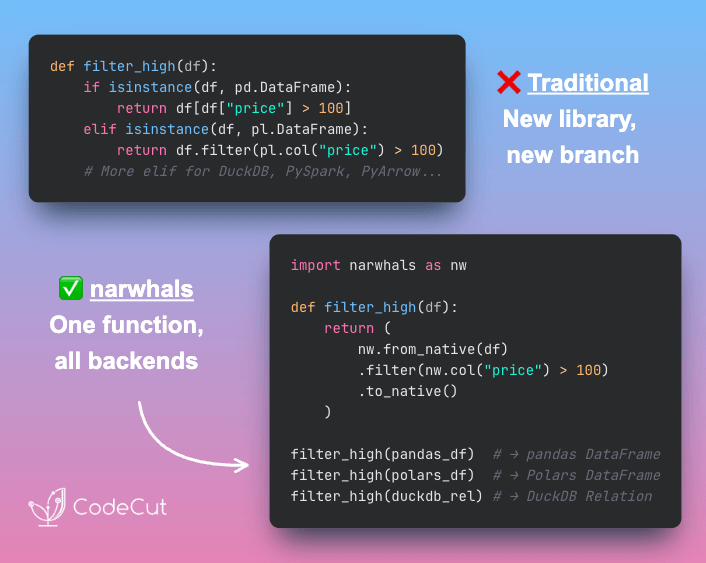
Narwhals: One Decorator for pandas, Polars, and DuckDB
Problem
Writing a DataFrame function that supports multiple libraries usually means maintaining separate versions of the same logic for each one.
If changes are needed, they need to be applied to every version.
Solution
With Narwhals‘ @narwhalify decorator, you write the logic once using a unified API.
The function then works with whatever DataFrame type is passed in and returns the same type, reducing friction when switching tools.
How is this different from Ibis? Ibis is built for data scientists switching between SQL backends. Narwhals is built for library authors who need their code to work with any DataFrame type.
Docling: Turn DOCX Reviewer Feedback into Structured Data
Problem
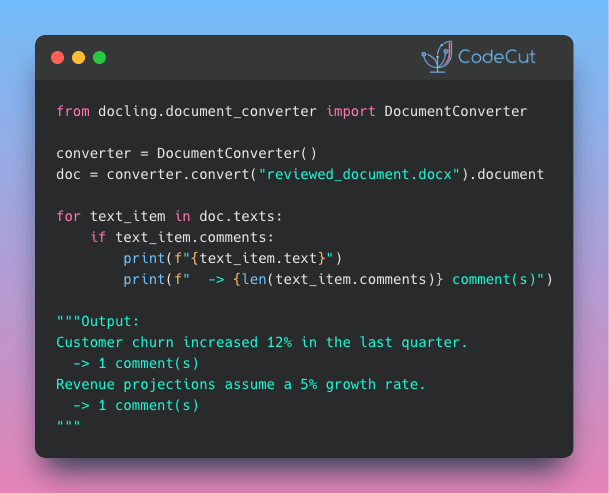
Pulling comments from Word files turns informal feedback into data you can analyze, manage, and act on in code.
Traditionally, this requires parsing raw XML and manually mapping each comment back to its referenced text.
Solution
Docling v2.71.0 simplifies this process. Converted documents now attach a comments field to every text item, making reviewer annotations accessible without manual XML handling.
This opens up workflows that were previously too tedious to automate:
Flag unresolved comments before merging document versions
Build dashboards tracking reviewer feedback across teams
Feed comment data into LLMs for sentiment analysis or summarization
📚 Latest Deep Dives
Portable DataFrames in Python: When to Use Ibis, Narwhals, or Fugue
– Write your DataFrame logic once and run it on any backend. Compare Ibis, Narwhals, and Fugue to find the right portability strategy for your Python workflow.
☕️ Weekly Finds
pdfGPT
[LLM]
– Chat with the contents of your PDF files using GPT capabilities and semantic search with sentence embeddings
SandDance
[Data Viz]
– Microsoft Research data visualization tool that maps every data row to a visual mark for interactive exploration
trafilatura
[Web Scraping]
– Python package and CLI for web crawling, scraping, and text extraction with output as CSV, JSON, HTML, or XML
Looking for a specific tool? Explore 70+ Python tools →
Stay Current with CodeCut
Actionable Python tips, curated for busy data pros. Skim in under 2 minutes, three times a week.
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-input {
background: #2F2D2E !important;
border: 1px solid #72BEFA !important;
color: #FFFFFF !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-input::placeholder {
color: #999999 !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-subscribe-btn {
background: #72BEFA !important;
color: #2F2D2E !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-subscribe-btn:hover {
background: #5aa8e8 !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form {
max-width: 650px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 8px;
}
.codecut-input {
-webkit-appearance: none;
-moz-appearance: none;
appearance: none;
background: #FFFFFF;
border-radius: 8px !important;
padding: 8px 12px;
font-family: ‘Comfortaa’, sans-serif !important;
font-size: 14px !important;
color: #333333;
border: none !important;
outline: none;
width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
input[type=”email”].codecut-input {
border-radius: 8px !important;
}
.codecut-input::placeholder {
color: #666666;
}
.codecut-email-row {
display: flex;
align-items: stretch;
height: 36px;
gap: 8px;
}
.codecut-email-row .codecut-input {
flex: 1;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn {
background: #72BEFA;
color: #2F2D2E;
border: none;
border-radius: 8px;
padding: 8px 14px;
font-family: ‘Comfortaa’, sans-serif;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
cursor: pointer;
text-decoration: none;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
transition: background 0.3s ease;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn:hover {
background: #5aa8e8;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn:disabled {
background: #999;
cursor: not-allowed;
}
.codecut-message {
font-family: ‘Comfortaa’, sans-serif;
font-size: 12px;
padding: 8px;
border-radius: 6px;
display: none;
}
.codecut-message.success {
background: #d4edda;
color: #155724;
display: block;
}
@media (max-width: 480px) {
.codecut-email-row {
flex-direction: column;
height: auto;
gap: 8px;
}
.codecut-input {
border-radius: 8px;
height: 36px;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn {
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 8px;
height: 36px;
}
}
Subscribe
Newsletter #291: Docling: Turn DOCX Reviewer Feedback into Structured Data Read More »