Newsletter #281: MarkItDown: From Images to Searchable Text in Seconds
Grab your coffee. Here are this week’s highlights.
🤝 COLLABORATION
What Data Engineers Really Think About Airflow (5.8K Surveyed)
Astronomer analyzed 5.8k+ responses from data engineers on how they are navigating Airflow today and the findings might surprise you.
You’ll learn:
How early adopters are using Airflow 3 features in production
Which teams are bringing AI into production and what’s holding others back
35.6% believe that Airflow is beneficial to their career
🔗 Download the State of Airflow 2026 Report
📅 Today’s Picks
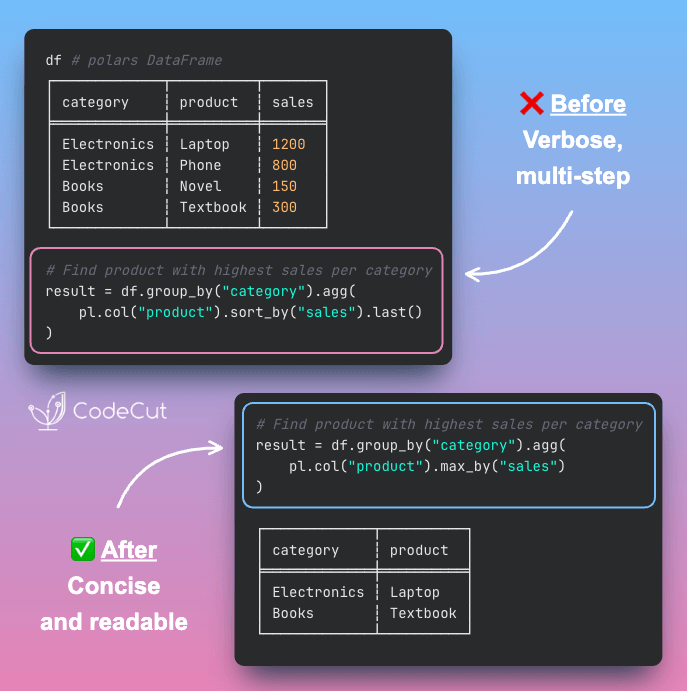
Query Multiple Databases at Once with DuckDB
Problem
Working with data across PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQLite often means managing multiple database connections and additional integration overhead.
That overhead adds up quickly when your goal is simply to analyze data across sources.
Solution
DuckDB removes the friction by allowing you to join tables across databases with a single query.
Key benefits:
Join SQLite, PostgreSQL, MySQL, and Parquet files in a single SQL statement
Automatic connection handling across all sources
Filters run at the source database, so only matching rows are transferred
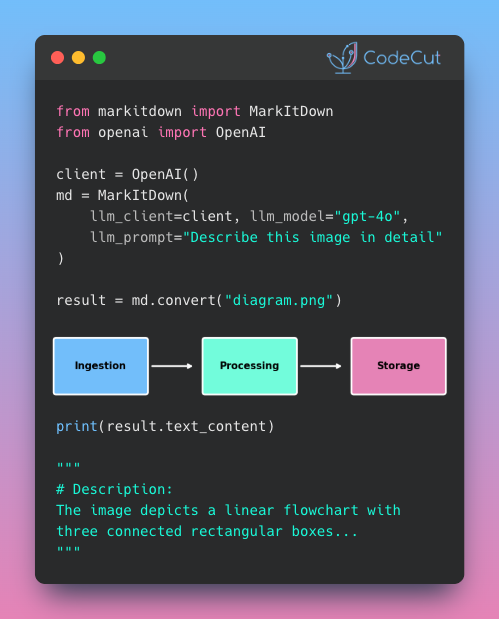
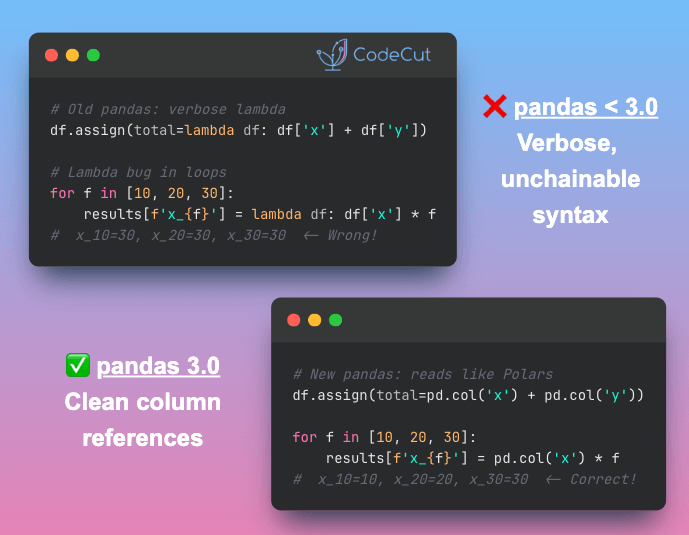
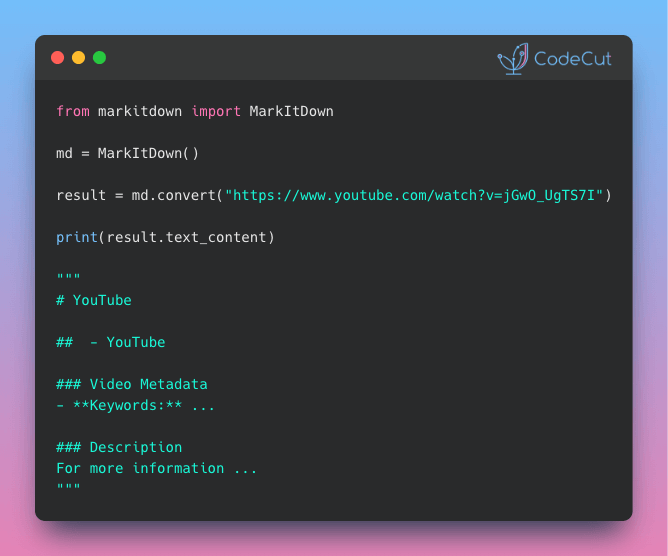
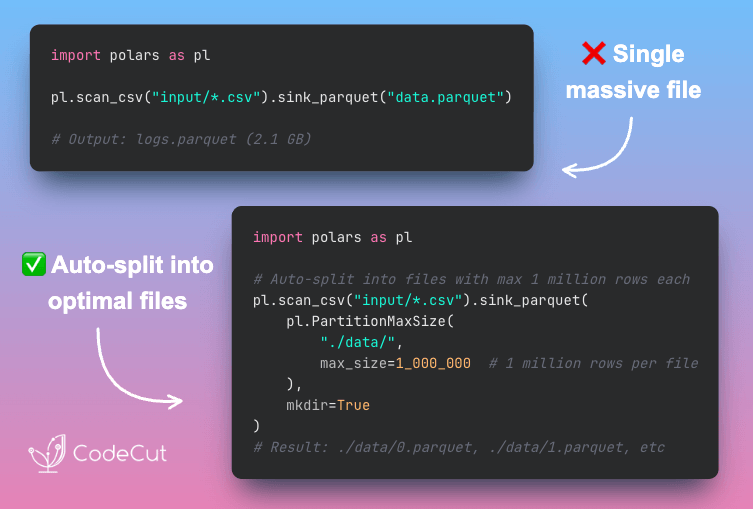
MarkItDown: From Images to Searchable Text in Seconds
Problem
Charts, diagrams, and screenshots in your documents need text descriptions to be searchable and processable.
But writing descriptions manually is slow and produces inconsistent results across large document sets.
Solution
MarkItDown, an open-source library from Microsoft, integrates with OpenAI to automatically generate detailed descriptions of images.
Key capabilities:
Generate consistent descriptions across hundreds of images
Process images from documents like PowerPoint and PDF files
Customize the description prompt for your specific needs
☕️ Weekly Finds
Skill_Seekers
[LLM]
– Convert documentation websites, GitHub repositories, and PDFs into Claude AI skills with automatic conflict detection
sqlit
[Data]
– A user-friendly TUI for SQL databases supporting SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Turso and more
giskard
[ML]
– Open-source CI/CD platform for ML teams to eliminate AI bias and deliver quality ML products faster
Looking for a specific tool? Explore 70+ Python tools →
📚 Latest Deep Dives
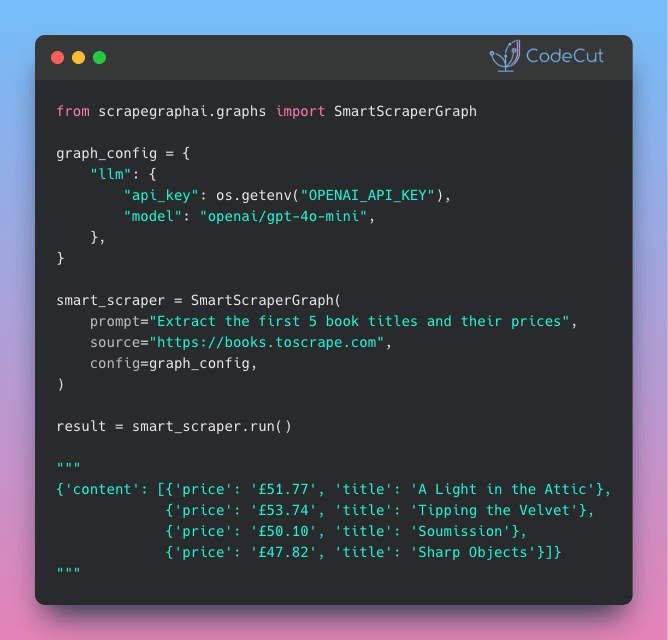
From CSS Selectors to Natural Language: Web Scraping with ScrapeGraphAI
– Web scraping without selector maintenance. ScrapeGraphAI uses LLMs to extract data from any site using plain English prompts and Pydantic schemas.
Stay Current with CodeCut
Actionable Python tips, curated for busy data pros. Skim in under 2 minutes, three times a week.
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-input {
background: #2F2D2E !important;
border: 1px solid #72BEFA !important;
color: #FFFFFF !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-input::placeholder {
color: #999999 !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-subscribe-btn {
background: #72BEFA !important;
color: #2F2D2E !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form .codecut-subscribe-btn:hover {
background: #5aa8e8 !important;
}
.codecut-subscribe-form {
max-width: 650px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 8px;
}
.codecut-input {
-webkit-appearance: none;
-moz-appearance: none;
appearance: none;
background: #FFFFFF;
border-radius: 8px !important;
padding: 8px 12px;
font-family: ‘Comfortaa’, sans-serif !important;
font-size: 14px !important;
color: #333333;
border: none !important;
outline: none;
width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
input[type=”email”].codecut-input {
border-radius: 8px !important;
}
.codecut-input::placeholder {
color: #666666;
}
.codecut-email-row {
display: flex;
align-items: stretch;
height: 36px;
gap: 8px;
}
.codecut-email-row .codecut-input {
flex: 1;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn {
background: #72BEFA;
color: #2F2D2E;
border: none;
border-radius: 8px;
padding: 8px 14px;
font-family: ‘Comfortaa’, sans-serif;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
cursor: pointer;
text-decoration: none;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
transition: background 0.3s ease;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn:hover {
background: #5aa8e8;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn:disabled {
background: #999;
cursor: not-allowed;
}
.codecut-message {
font-family: ‘Comfortaa’, sans-serif;
font-size: 12px;
padding: 8px;
border-radius: 6px;
display: none;
}
.codecut-message.success {
background: #d4edda;
color: #155724;
display: block;
}
@media (max-width: 480px) {
.codecut-email-row {
flex-direction: column;
height: auto;
gap: 8px;
}
.codecut-input {
border-radius: 8px;
height: 36px;
}
.codecut-subscribe-btn {
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 8px;
height: 36px;
}
}
Subscribe
Newsletter #281: MarkItDown: From Images to Searchable Text in Seconds Read More »